Do cancer biomarkers make targeted therapies cost-effective? A systematic review in metastatic colorectal cancer
- PMID: 30256829
- PMCID: PMC6157891
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0204496
Do cancer biomarkers make targeted therapies cost-effective? A systematic review in metastatic colorectal cancer
Abstract
Background: Recent advances in targeted therapies have raised expectations that the clinical application of biomarkers would improve patient's health outcomes and potentially save costs. However, the cost-effectiveness of biomarkers remains unclear irrespective of the cost-effectiveness of corresponding therapies. It is thus important to determine whether biomarkers for targeted therapies provide good value for money. This study systematically reviews economic evaluations of biomarkers for targeted therapies in metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) and assesses the cost-effectiveness of predictive biomarkers in mCRC.
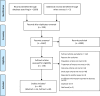
Methods: A literature search was performed using Medline, Embase, EconLit, NHSEED. Papers published from 2000 until June 2018 were searched. All economic evaluations assessing biomarker-guided therapies with companion diagnostics in mCRC were searched. To make studies more comparable, cost-effectiveness results were synthesized as per biomarker tests and corresponding therapies. Methodological quality was assessed using the Quality of Health Economic Studies (QHES) instrument.
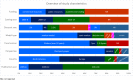
Results: Forty-six studies were included in this review. Of these, 17 studies evaluated the intrinsic value of cancer biomarkers, whereas the remaining studies focused on assessing the cost-effectiveness of corresponding drugs. Most studies indicated favourable cost-effectiveness of biomarkers for targeted therapies in mCRC. Some studies reported that biomarkers were cost-effective, while their corresponding therapies were not cost-effective. A considerable number of economic evaluations were conducted in pre-defined genetic populations and thus, often failed to fully capture the biomarker's clinical and economic values. The average QHES score was 73.6.
Conclusion: Cancer biomarkers for targeted therapies in mCRC were mostly found to be cost-effective; otherwise, they at least improved the cost-effectiveness of targeted therapies by saving some costs. However, this did not necessarily make their corresponding therapies cost-effective. While companion biomarkers reduced therapy costs, the savings were not sufficient to make the corresponding agents cost-effective. Evaluation of biomarkers was often restricted to the cost of tests and did not consider their clinical values or biomarker prevalence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
How are we evaluating the cost-effectiveness of companion biomarkers for targeted cancer therapies? A systematic review.BMC Cancer. 2021 Sep 1;21(1):980. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08725-4. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34470603 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-Effectiveness of RAS Genetic Testing Strategies in Patients With Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review.Value Health. 2020 Jan;23(1):114-126. doi: 10.1016/j.jval.2019.07.009. Epub 2019 Sep 3. Value Health. 2020. PMID: 31952666
-
KRAS Testing for Anti-EGFR Therapy in Advanced Colorectal Cancer: An Evidence-Based and Economic Analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2010;10(25):1-49. Epub 2010 Dec 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2010. PMID: 23074403 Free PMC article.
-
The evolution of biomarkers to guide the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer.Am J Manag Care. 2018 Apr;24(7 Suppl):S107-S117. Am J Manag Care. 2018. PMID: 30207665
-
Cost-effectiveness analysis of screening for KRAS and BRAF mutations in metastatic colorectal cancer.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2012 Dec 5;104(23):1785-95. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djs433. Epub 2012 Nov 28. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2012. PMID: 23197490 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Advantages of the Combinatorial Molecular Targeted Therapy of Head and Neck Cancer-A Step before Anakoinosis-Based Personalized Treatment.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Aug 24;15(17):4247. doi: 10.3390/cancers15174247. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37686523 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Consensus Statements on Precision Oncology in the China Greater Bay Area.JCO Precis Oncol. 2023 Jun;7:e2200649. doi: 10.1200/PO.22.00649. JCO Precis Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37315266 Free PMC article.
-
A Practical Guide to Modeling and Conducting a Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Companion Biomarker Tests for Targeted Therapies Using R: Tutorial Paper.Pharmacoeconomics. 2021 Dec;39(12):1373-1381. doi: 10.1007/s40273-021-01069-8. Epub 2021 Aug 20. Pharmacoeconomics. 2021. PMID: 34414545 Free PMC article.
-
Herbal melanin inhibits colorectal cancer cell proliferation by altering redox balance, inducing apoptosis, and modulating MAPK signaling.Cancer Cell Int. 2020 Apr 16;20:126. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-01206-x. eCollection 2020. Cancer Cell Int. 2020. PMID: 32322173 Free PMC article.
-
Very Early Health Technology Assessment for Potential Predictive Biomarkers in the Treatment of Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Pharmacoecon Open. 2025 May;9(3):471-485. doi: 10.1007/s41669-025-00557-3. Epub 2025 Jan 28. Pharmacoecon Open. 2025. PMID: 39875696 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stewart B, Wild C. World cancer report 2014 Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer, WHO; 2014. 2015.
-
- Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians. 2014;64(1):9–29. - PubMed
-
- Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW. The genetic basis of human cancer McGraw-Hill; 2002.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous