Predialysis anemia management and outcomes following dialysis initiation: A retrospective cohort analysis
- PMID: 30256836
- PMCID: PMC6157862
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0203767
Predialysis anemia management and outcomes following dialysis initiation: A retrospective cohort analysis
Abstract
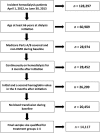
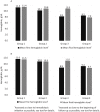
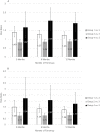
Whether and how anemia treatment with erythropoiesis stimulating agents (ESAs) before hemodialysis initiation may be associated with lower mortality after dialysis initiation is unknown. We compared all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in two groups of patients who experienced distinct anemia treatment patterns with ESAs before and after hemodialysis initiation. This retrospective cohort analysis included patients initiating hemodialysis April 1, 2012-June 30, 2013, identified from United States Renal Data System end-stage renal disease (ESRD) and pre-ESRD files. Patients treated with ESAs before and after hemodialysis initiation who maintained Hb ≥ 9.0 g/dL throughout (comparator group, n = 3662) were compared with patients with Hb < 9.0 g/dL before hemodialysis initiation (with or without ESAs) whose levels increased with ESAs after hemodialysis initiation (referent group, n = 4461). Cox proportional hazards models were used to calculate the hazard ratio of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality after hemodialysis initiation. Of 20,454 patients, 4855 (23.7%) had Hb < 9.0 g/dL upon hemodialysis initiation; of these 4855, 26.6% received ESAs before initiation. Comparator group Hb levels increased from 8.2 ± 0.8 mg/dL upon initiation to 10.9 ± 1.2 with ESAs afterward. Comparator patients were more likely than referent patients to be younger (76.3 ± 6.7 versus 77.2 ± 6.9 years), male (51.5% versus 49.8%), and black (24.6% versus 18.6%). Risk of all-cause mortality was lower for the comparator group versus the referent group at 3 (HR 0.83, 95% CI 0.68-1.00, P = 0.052), 6 (0.86, 0.74-1.00, P = 0.047), and 12 (0.88, 0.78-0.99, P = 0.036) months. The pattern was similar for cardiovascular mortality. Hb ≥ 9.0 with ESAs before and after hemodialysis initiation was generally associated with lower post-initiation all-cause and cardiovascular mortality compared with predialysis Hb < 9.0 g/dL in patients whose Hb levels subsequently improved with ESAs after hemodialysis initiation.
Conflict of interest statement
HX and MVS are employed by AstraZeneca. DTG has provided statistical consultation to DaVita Clinical Research. JBW, SL, YP, HY, and JL report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anemia Treatment by Erythropoiesis-stimulating Agents during the 6 Months before the Initiation of Hemodialysis: Comparison of Darbepoetin Alfa and Continuous Erythropoietin Receptor Activator.Keio J Med. 2017 Sep 26;66(3):44-50. doi: 10.2302/kjm.2016-0009-OA. Epub 2016 Dec 19. Keio J Med. 2017. PMID: 27990008
-
2008 Japanese Society for Dialysis Therapy: guidelines for renal anemia in chronic kidney disease.Ther Apher Dial. 2010 Jun;14(3):240-75. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-9987.2010.00836.x. Ther Apher Dial. 2010. PMID: 20609178
-
Comparative mortality risk of anemia management practices in incident hemodialysis patients.JAMA. 2010 Mar 3;303(9):857-64. doi: 10.1001/jama.2010.206. JAMA. 2010. PMID: 20197532
-
Simplifying anemia management in hemodialysis patients: ESAs administered at longer dosing intervals can enhance opportunities to provide patient-focused care.Curr Med Res Opin. 2011 Aug;27(8):1539-50. doi: 10.1185/03007995.2011.588202. Epub 2011 Jun 17. Curr Med Res Opin. 2011. PMID: 21682552 Review.
-
Effectiveness of Darbepoetin Alfa for Chemotherapy-induced Anemia When Initiated at Hemoglobin ≤10 g/dL.Clin Ther. 2016 Jan 1;38(1):122-135.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2015.11.012. Epub 2015 Dec 22. Clin Ther. 2016. PMID: 26730453 Review.
Cited by
-
Factors affecting pre-end-stage kidney disease haemoglobin control and outcomes following dialysis initiation: a nationwide study.Clin Kidney J. 2021 Feb 5;14(7):1780-1788. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfaa213. eCollection 2021 Jul. Clin Kidney J. 2021. PMID: 34221385 Free PMC article.
-
Association between admission hemoglobin level and prognosis in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.World J Diabetes. 2021 Nov 15;12(11):1917-1927. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v12.i11.1917. World J Diabetes. 2021. PMID: 34888016 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of hypoxia-inducible factor-prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors on anemia in patients with CKD: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials including 2804 patients.Ren Fail. 2020 Nov;42(1):912-925. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2020.1811121. Ren Fail. 2020. PMID: 32869703 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of anemia in predialysis chronic kidney disease: Is the study center a significant factor?PLoS One. 2020 Apr 2;15(4):e0230980. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0230980. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32240223 Free PMC article.
-
Low hemoglobin at hemodialysis initiation: an international study of anemia management and mortality in the early dialysis period.Clin Kidney J. 2019 Jul 5;13(3):425-433. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfz065. eCollection 2020 Jun. Clin Kidney J. 2019. PMID: 32699623 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Astor BC, Muntner P, Levin A, Eustace JA, Coresh J. Association of kidney function with anemia: the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (1988–1994). Arch Intern Med. 2002;162: 1401–1408. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

