Common psychiatric and metabolic comorbidity of adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: A population-based cross-sectional study
- PMID: 30256837
- PMCID: PMC6157884
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0204516
Common psychiatric and metabolic comorbidity of adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: A population-based cross-sectional study
Abstract
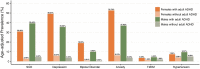
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is often comorbid with other psychiatric conditions in adults. Yet, less is known about its relationship with common metabolic disorders and how sex and ageing affect the overall comorbidity patterns of adult ADHD. We aimed to examine associations of adult ADHD with several common psychiatric and metabolic conditions. Through the linkage of multiple Swedish national registers, 5,551,807 adults aged 18 to 64 years and living in Sweden on December 31, 2013 were identified and assessed for clinical diagnoses of adult ADHD, substance use disorder (SUD), depression, bipolar disorder, anxiety, type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), and hypertension. Logistic regression models and regression standardization method were employed to obtain estimates of prevalence, prevalence difference (PD), and prevalence ratio (PR). All comorbid conditions of interest were more prevalent in adults with ADHD (3.90% to 44.65%) than in those without (0.72% to 4.89%), with the estimated PRs being over nine for psychiatric conditions (p < 0.001) and around two for metabolic conditions (p < 0.001). Sex differences in the prevalence of comorbidities were observed among adults with ADHD. Effect modification by sex was detected on the additive scale and/or multiplicative scale for the associations of adult ADHD with all comorbidities. ADHD remained associated with all comorbidities in older adults aged 50 to 64 when all conditions were assessed from age 50 onwards. The comorbidity patterns of adult ADHD underscore the severity and clinical complexity of the disorder. Clinicians should remain vigilant for a wide range of psychiatric and metabolic problems in ADHD affected adults of all ages and both sexes.
Conflict of interest statement
In the past year, Dr. Faraone received income, potential income, travel expenses continuing education support and/or research support from Otsuka, Lundbeck, KenPharm, Rhodes, Arbor, Ironshore, Shire, Akili Interactive Labs, CogCubed, Alcobra, VAYA, Sunovion, Genomind and NeuroLifeSciences. With his institution, he has US patent US20130217707 A1 for the use of sodium-hydrogen exchange inhibitors in the treatment of ADHD. Dr. Larsson has served as a speaker for Eli-Lilly and has received research grants from Shire. Dr. Haavik has served as a speaker for Eli-Lilly, HB Pharma and Shire. The other authors declare no competing interests. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gender differences in psychiatric comorbidity: a population-based study of 40 000 adults with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder.Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2018 Mar;137(3):176-186. doi: 10.1111/acps.12845. Epub 2017 Dec 21. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2018. PMID: 29266167 Free PMC article.
-
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, other mental health problems, substance use, and driving: examination of a population-based, representative canadian sample.Traffic Inj Prev. 2014;15 Suppl 1:S1-9. doi: 10.1080/15389588.2014.926341. Traffic Inj Prev. 2014. PMID: 25307372
-
A Cross-sectional Cohort Study of Prevalence, Co-Morbidities, and Correlates of Attention-deficit Hyperactivity Disorder among Adult Patients Admitted to the Li Ka Shing Psychiatric Outpatient Clinic, Hong Kong.East Asian Arch Psychiatry. 2017 Jun;27(2):63-70. East Asian Arch Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 28652499
-
Comorbidity of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder with psychiatric disorder: an overview.J Clin Psychiatry. 1998;59 Suppl 7:50-8. J Clin Psychiatry. 1998. PMID: 9680053 Review.
-
Adult ADHD and its comorbidities, with a focus on bipolar disorder.J Affect Disord. 2010 Jul;124(1-2):1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2009.06.036. Epub 2009 Aug 15. J Affect Disord. 2010. PMID: 19683348 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of Paroxetine, a Strong CYP2D6 Inhibitor, on SPN-812 (Viloxazine Extended-Release) Pharmacokinetics in Healthy Adults.Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2021 Nov;10(11):1365-1374. doi: 10.1002/cpdd.948. Epub 2021 May 4. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2021. PMID: 33943033 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment provision for adults with ADHD during the COVID-19 pandemic: an exploratory study on patient and therapist experience with on-site sessions using face masks vs. telepsychiatric sessions.BMC Psychiatry. 2021 May 5;21(1):237. doi: 10.1186/s12888-021-03236-9. BMC Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 33952229 Free PMC article.
-
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder symptoms and subsequent cardiometabolic disorders in adults: investigating underlying mechanisms using a longitudinal twin study.BMC Med. 2023 Nov 22;21(1):452. doi: 10.1186/s12916-023-03174-1. BMC Med. 2023. PMID: 37993878 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of emotional dysregulation and comorbid depressive symptoms on clinical features, brain arousal, and treatment response in adults with ADHD.Front Psychiatry. 2024 Jan 5;14:1294314. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1294314. eCollection 2023. Front Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38250266 Free PMC article.
-
Patterns of Psychiatric Comorbidity and Genetic Correlations Provide New Insights Into Differences Between Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder and Autism Spectrum Disorder.Biol Psychiatry. 2019 Oct 15;86(8):587-598. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2019.04.021. Epub 2019 Apr 28. Biol Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 31182215 Free PMC article.
References
-
- van de Glind G, Konstenius M, Koeter MW, van Emmerik-van Oortmerssen K, Carpentier PJ, Kaye S, et al. Variability in the prevalence of adult ADHD in treatment seeking substance use disorder patients: results from an international multi-center study exploring DSM-IV and DSM-5 criteria. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2014;134:158–66. Epub 2013/10/26. 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2013.09.026 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials