Copper transporter ATP7A interacts with IQGAP1, a Rac1 binding scaffolding protein: role in PDGF-induced VSMC migration and vascular remodeling
- PMID: 30257103
- PMCID: PMC6336942
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00230.2018
Copper transporter ATP7A interacts with IQGAP1, a Rac1 binding scaffolding protein: role in PDGF-induced VSMC migration and vascular remodeling
Abstract
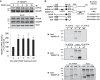
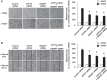
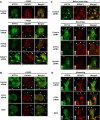
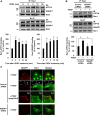
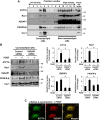
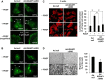
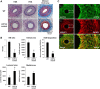
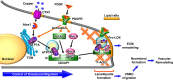
Vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) migration contributes to neointimal formation after vascular injury. We previously demonstrated that copper (Cu) transporter ATP7A is involved in platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-induced VSMC migration in a Cu- and Rac1-dependent manner. The underlying mechanism is still unknown. Here we show that ATP7A interacts with IQGAP1, a Rac1 and receptor tyrosine kinase binding scaffolding proteins, which mediates PDGF-induced VSMC migration and vascular remodeling. In cultured rat aortic SMCs, PDGF stimulation rapidly promoted ATP7A association with IQGAP1 and Rac1 and their translocation to the lipid rafts and leading edge. Cotransfection assay revealed that ATP7A directly bound to NH2-terminal domain of IQGAP1. Functionally, either ATP7A or IQGAP1 depletion using siRNA significantly inhibited PDGF-induced VSMC migration without additive effects, suggesting that IQGAP1 and ATP7A are in the same axis to promote migration. Furthermore, IQGAP1 siRNA blocked PDGF-induced ATP7A association with Rac1 as well as its translocation to leading edge, while PDGF-induced IQGAP1 translocation was not affected by ATP7A siRNA or Cu chelator. Overexpression of mutant IQGAP1 lacking a Rac1 binding site prevented PDGF-induced translocation of Rac1, but not ATP7A, to the leading edge, thereby inhibiting lamellipodia formation and VSMC migration. In vivo, ATP7A colocalized with IQGAP1 at neointimal VSMCs in a mice wire injury model, while neointimal formation and extracellular matrix deposition induced by vascular injury were inhibited in ATP7A mutant mice with reduced Cu transporter function. In summary, IQGAP1 functions as ATP7A and Rac1 binding scaffolding protein to organize PDGF-dependent ATP7A translocation to the lamellipodial leading edge, thereby promoting VSMC migration and vascular remodeling.
Keywords: copper transporter; migration; platelet-derived growth factor; vascular remodeling; vascular smooth muscle.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Unexpected role of the copper transporter ATP7A in PDGF-induced vascular smooth muscle cell migration.Circ Res. 2010 Sep 17;107(6):787-99. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.225334. Epub 2010 Jul 29. Circ Res. 2010. PMID: 20671235 Free PMC article.
-
Novel role of copper transport protein antioxidant-1 in neointimal formation after vascular injury.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013 Apr;33(4):805-13. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.300862. Epub 2013 Jan 24. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013. PMID: 23349186 Free PMC article.
-
IQGAP1 links PDGF receptor-β signal to focal adhesions involved in vascular smooth muscle cell migration: role in neointimal formation after vascular injury.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013 Sep 15;305(6):C591-600. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00011.2013. Epub 2013 May 8. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23657573 Free PMC article.
-
New model for the interaction of IQGAP1 with CDC42 and RAC1.Small GTPases. 2020 Jan;11(1):16-22. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2017.1321169. Epub 2017 Jun 19. Small GTPases. 2020. PMID: 28622072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Animal Models of Neointimal Hyperplasia and Restenosis: Species-Specific Differences and Implications for Translational Research.JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2021 Aug 11;6(11):900-917. doi: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2021.06.006. eCollection 2021 Nov. JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2021. PMID: 34869956 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Vav2 promotes ductus arteriosus anatomic closure via the remodeling of smooth muscle cells by Rac1 activation.J Mol Med (Berl). 2023 Dec;101(12):1567-1585. doi: 10.1007/s00109-023-02377-6. Epub 2023 Oct 7. J Mol Med (Berl). 2023. PMID: 37804474
-
Identification of core cuprotosis-correlated biomarkers in abdominal aortic aneurysm immune microenvironment based on bioinformatics.Front Immunol. 2023 Apr 17;14:1138126. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1138126. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37138870 Free PMC article.
-
The Multifaceted Roles of Copper in Cancer: A Trace Metal Element with Dysregulated Metabolism, but Also a Target or a Bullet for Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Dec 1;12(12):3594. doi: 10.3390/cancers12123594. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33271772 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiac copper content and its relationship with heart physiology: Insights based on quantitative genetic and functional analyses using BXD family mice.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Feb 2;10:1089963. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1089963. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 36818345 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation of Ultra-Small Copper Nanoparticles-Loaded Self-Healing Hydrogels with Antibacterial, Inflammation-Suppressing and Angiogenesis-Enhancing Properties for Promoting Diabetic Wound Healing.Int J Nanomedicine. 2023 Jun 19;18:3339-3358. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S399933. eCollection 2023. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023. PMID: 37361387 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allen WE, Jones GE, Pollard JW, Ridley AJ. Rho, Rac and Cdc42 regulate actin organization and cell adhesion in macrophages. J Cell Sci 110: 707–720, 1997. - PubMed
-
- Ashino T, Sudhahar V, Urao N, Oshikawa J, Chen GF, Wang H, Huo Y, Finney L, Vogt S, McKinney RD, Maryon EB, Kaplan JH, Ushio-Fukai M, Fukai T. Unexpected role of the copper transporter ATP7A in PDGF-induced vascular smooth muscle cell migration. Circ Res 107: 787–799, 2010. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.225334. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brasselet C, Durand E, Addad F, Al Haj Zen A, Smeets MB, Laurent-Maquin D, Bouthors S, Bellon G, de Kleijn D, Godeau G, Garnotel R, Gogly B, Lafont A. Collagen and elastin cross-linking: a mechanism of constrictive remodeling after arterial injury. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 289: H2228–H2233, 2005. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00410.2005. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

