Thermophilic Proteins as Versatile Scaffolds for Protein Engineering
- PMID: 30257429
- PMCID: PMC6313779
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms6040097
Thermophilic Proteins as Versatile Scaffolds for Protein Engineering
Abstract
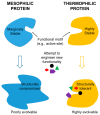
Literature from the past two decades has outlined the existence of a trade-off between protein stability and function. This trade-off creates a unique challenge for protein engineers who seek to introduce new functionality to proteins. These engineers must carefully balance the mutation-mediated creation and/or optimization of function with the destabilizing effect of those mutations. Subsequent research has shown that protein stability is positively correlated with "evolvability" or the ability to support mutations which bestow new functionality on the protein. Since the ultimate goal of protein engineering is to create and/or optimize a protein's function, highly stable proteins are preferred as potential scaffolds for protein engineering. This review focuses on the application potential for thermophilic proteins as scaffolds for protein engineering. The relatively high inherent thermostability of these proteins grants them a great deal of mutational robustness, making them promising scaffolds for various protein engineering applications. Comparative studies on the evolvability of thermophilic and mesophilic proteins have strongly supported the argument that thermophilic proteins are more evolvable than mesophilic proteins. These findings indicate that thermophilic proteins may represent the scaffold of choice for protein engineering in the future.
Keywords: evolvability; protein engineering; protein stability; thermophilic proteins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Engineering Strategies to Overcome the Stability-Function Trade-Off in Proteins.ACS Synth Biol. 2022 Mar 18;11(3):1030-1039. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.1c00512. Epub 2022 Mar 8. ACS Synth Biol. 2022. PMID: 35258287 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Determinants of Developability and Evolvability of Synthetic Miniproteins as Ligand Scaffolds.J Mol Biol. 2023 Dec 15;435(24):168339. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2023.168339. Epub 2023 Nov 3. J Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37923119 Free PMC article.
-
Charge reversal mutations in mesophilic-thermophilic orthologous protein pairs and their role in enhancing coulombic interaction energy.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2023 Mar;41(5):1745-1752. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2021.2024258. Epub 2022 Jan 7. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2023. PMID: 34996344
-
Statistical Analysis of the Role of Cavity Flexibility in Thermostability of Proteins.Polymers (Basel). 2024 Jan 21;16(2):291. doi: 10.3390/polym16020291. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38276699 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in amino acids composition and coupling patterns between mesophilic and thermophilic proteins.Amino Acids. 2008 Jan;34(1):25-33. doi: 10.1007/s00726-007-0589-x. Epub 2007 Aug 21. Amino Acids. 2008. PMID: 17710363 Review.
Cited by
-
Abridgement of Microbial Esterases and Their Eminent Industrial Endeavors.Mol Biotechnol. 2025 Mar;67(3):817-833. doi: 10.1007/s12033-024-01108-7. Epub 2024 Mar 9. Mol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 38461181 Review.
-
Phospholipid N-Methyltransferases Produce Various Methylated Phosphatidylethanolamine Derivatives in Thermophilic Bacteria.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2021 Sep 10;87(19):e0110521. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01105-21. Epub 2021 Sep 10. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34288711 Free PMC article.
-
Extremophiles, a Nifty Tool to Face Environmental Pollution: From Exploitation of Metabolism to Genome Engineering.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 May 14;18(10):5228. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18105228. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34069056 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Dynamics Simulations of HPr Proteins from a Thermophilic and a Mesophilic Organism: A Comparative Thermal Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 31;24(11):9557. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119557. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37298508 Free PMC article.
-
Alkaliphilic/Alkali-Tolerant Fungi: Molecular, Biochemical, and Biotechnological Aspects.J Fungi (Basel). 2023 Jun 9;9(6):652. doi: 10.3390/jof9060652. J Fungi (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37367588 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous