Discovery of CNS-Like D3R-Selective Antagonists Using 3D Pharmacophore Guided Virtual Screening
- PMID: 30257450
- PMCID: PMC6222863
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules23102452
Discovery of CNS-Like D3R-Selective Antagonists Using 3D Pharmacophore Guided Virtual Screening
Abstract
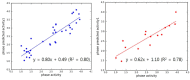
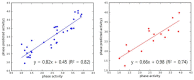
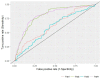
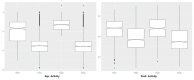
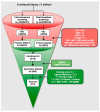
The dopamine D3 receptor is an important CNS target for the treatment of a variety of neurological diseases. Selective dopamine D3 receptor antagonists modulate the improvement of psychostimulant addiction and relapse. In this study, five and six featured pharmacophore models of D3R antagonists were generated and evaluated with the post-hoc score combining two survival scores of active and inactive. Among the Top 10 models, APRRR215 and AHPRRR104 were chosen based on the coefficient of determination (APRRR215: R²training = 0.80; AHPRRR104: R²training = 0.82) and predictability (APRRR215: Q²test = 0.73, R²predictive = 0.82; AHPRRR104: Q²test = 0.86, R²predictive = 0.74) of their 3D-quantitative structure⁻activity relationship models. Pharmacophore-based virtual screening of a large compound library from eMolecules (>3 million compounds) using two optimal models expedited the search process by a 100-fold speed increase compared to the docking-based screening (HTVS scoring function in Glide) and identified a series of hit compounds having promising novel scaffolds. After the screening, docking scores, as an adjuvant predictor, were added to two fitness scores (from the pharmacophore models) and predicted Ki (from PLSs of the QSAR models) to improve accuracy. Final selection of the most promising hit compounds were also evaluated for CNS-like properties as well as expected D3R antagonism.
Keywords: 3D-QSAR; CNS-like; D3R selective antagonist; molecular docking; pharmacophore; virtual screening.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identifying Dopamine D3 Receptor Ligands through Virtual Screening and Exploring the Binding Modes of Hit Compounds.Molecules. 2023 Jan 5;28(2):527. doi: 10.3390/molecules28020527. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36677583 Free PMC article.
-
Studies of new fused benzazepine as selective dopamine D3 receptor antagonists using 3D-QSAR, molecular docking and molecular dynamics.Int J Mol Sci. 2011 Feb 18;12(2):1196-221. doi: 10.3390/ijms12021196. Int J Mol Sci. 2011. PMID: 21541053 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacophore Based 3D-QSAR, Virtual Screening and Docking Studies on Novel Series of HDAC Inhibitors with Thiophen Linker as Anticancer Agents.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2016;19(9):735-751. doi: 10.2174/1386207319666160801154415. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2016. PMID: 27487787
-
Targeting the dopamine D3 receptor: an overview of drug design strategies.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2016 Jul;11(7):641-64. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2016.1185413. Epub 2016 May 30. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2016. PMID: 27135354 Review.
-
Neuronal Dopamine D3 Receptors: Translational Implications for Preclinical Research and CNS Disorders.Biomolecules. 2021 Jan 14;11(1):104. doi: 10.3390/biom11010104. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33466844 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
3D-QSAR Studies of 1,2,4-Oxadiazole Derivatives as Sortase A Inhibitors.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Dec 6;2021:6380336. doi: 10.1155/2021/6380336. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34912894 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Predictive Models for Identifying Potential S100A9 Inhibitors Based on Machine Learning Methods.Front Chem. 2019 Nov 25;7:779. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2019.00779. eCollection 2019. Front Chem. 2019. PMID: 31824919 Free PMC article.
-
Computational approaches for the design of novel dopamine D2 and serotonin 5-HT2A receptor dual antagonist towards schizophrenia.In Silico Pharmacol. 2022 Apr 8;10(1):7. doi: 10.1007/s40203-022-00121-5. eCollection 2022. In Silico Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35433192 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Phytoconstituents as Potent Inhibitors of Casein Kinase-1 Alpha Using Virtual Screening and Molecular Dynamics Simulations.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Dec 15;13(12):2157. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13122157. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34959438 Free PMC article.
-
In Silico Repositioning of Dopamine Modulators with Possible Application to Schizophrenia: Pharmacophore Mapping, Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Analysis.ACS Omega. 2021 Jun 1;6(23):14748-14764. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c05984. eCollection 2021 Jun 15. ACS Omega. 2021. PMID: 34151057 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

