Efficacy and safety of alirocumab in Korean patients with hypercholesterolemia and high cardiovascular risk: subanalysis of the ODYSSEY-KT study
- PMID: 30257549
- PMCID: PMC6823573
- DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2018.133
Efficacy and safety of alirocumab in Korean patients with hypercholesterolemia and high cardiovascular risk: subanalysis of the ODYSSEY-KT study
Abstract
Background/aims: Efficacy and safety data of alirocumab, a fully human monoclonal antibody to proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9), is not yet well established in the Korean population. We assessed them in ODYSSEY-KT through the pre-specified Korean subanalysis.
Methods: In the ODYSSEY-KT study, South Korean and Taiwanese patients with hypercholesterolemia and high cardiovascular risks were randomized (1:1) to alirocumab or placebo. Alirocumab was self-administered subcutaneously at 75 mg every 2 weeks with a maximally tolerated statin dose with or without other lipid-modifying therapies. Alirocumab dose was increased to 150 mg every 2 weeks at week 12 if low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) ≥ 70 mg/dL at week 8. Primary endpoint was percent change in LDL-C from baseline to week 24. Results from Korean cohort (n = 83: 40 for alirocumab and 43 for placebo, respectively) analyses are reported here.
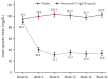
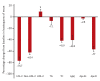
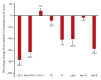
Results: In alirocumab group, the least square of mean change percent in LDL-C levels was -65.7% (placebo: 11.1%; p < 0.0001) and 92.0% of them achieved LDL-C < 70 mg/dL (placebo: 12.7%; p < 0.0001) at week 24. Alirocumab also showed significantly greater improvements in high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), non-HDL-C, total cholesterol, lipoprotein(a), and apolipoprotein B than placebo (p < 0.05). Two consecutive calculated LDL-C values < 25 mg/dL were observed in 37.5% of alirocumab-treated patients. Overall, 45.0% alirocumab-treated and 51.2% placebo-treated patients experienced treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) without discontinuation of treatment due to TEAEs.
Conclusion: Alirocumab has demonstrated to be effective in improvement of LDL-C and related lipid profiles in Korean cohort. Alirocumab was generally well tolerated with no significant safety signals.
Keywords: Cholesterol, LDL; Hypercholesterolemia; ODYSSEY; PCSK9.
Conflict of interest statement
This study was funded by Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Program for prevention and management of a cardio-cerebrovascular disease [Internet] Cheongju (KR): KCDC; 2017. 2017 [cited 2018 Aug 11]. Available from: http://www.cdc.go.kr/CDC/eng/contents/CdcEngContent-View.jsp?cid=74261&m....
-
- Korean Society of Lipidology and Atherosclerosis . Dyslipidemia fact sheet in Korea [Internet] Seoul (KR): Korean Society of Lipidology and Atherosclerosis; c2015. [cited 2018 Aug 11]. Available from: http://www.lipid.or.kr/file/Dyslipidemia%20fact%20sheet_eng_Final.pdf.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
