Cold shock proteins: from cellular mechanisms to pathophysiology and disease
- PMID: 30257675
- PMCID: PMC6158828
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-018-0274-6
Cold shock proteins: from cellular mechanisms to pathophysiology and disease
Abstract
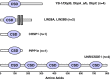
Cold shock proteins are multifunctional RNA/DNA binding proteins, characterized by the presence of one or more cold shock domains. In humans, the best characterized members of this family are denoted Y-box binding proteins, such as Y-box binding protein-1 (YB-1). Biological activities range from the regulation of transcription, splicing and translation, to the orchestration of exosomal RNA content. Indeed, the secretion of YB-1 from cells via exosomes has opened the door to further potent activities. Evidence links a skewed cold shock protein expression pattern with cancer and inflammatory diseases. In this review the evidence for a causative involvement of cold shock proteins in disease development and progression is summarized. Furthermore, the potential application of cold shock proteins for diagnostics and as targets for therapy is elucidated.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

References
-
- Wolffe AP, Tafuri S, Ranjan M, Familari M. The Y-box factors: a family of nucleic acid binding proteins conserved from Escherichia coli to man. New Biol. 1992;4(4):290–298. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

