Genomic insights into chromatin reprogramming to totipotency in embryos
- PMID: 30257850
- PMCID: PMC6314560
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201807044
Genomic insights into chromatin reprogramming to totipotency in embryos
Abstract
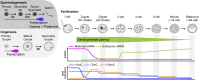
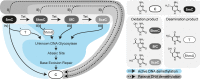
The early embryo is the natural prototype for the acquisition of totipotency, which is the potential of a cell to produce a whole organism. Generation of a totipotent embryo involves chromatin reorganization and epigenetic reprogramming that alter DNA and histone modifications. Understanding embryonic chromatin architecture and how this is related to the epigenome and transcriptome will provide invaluable insights into cell fate decisions. Recently emerging low-input genomic assays allow the exploration of regulatory networks in the sparsely available mammalian embryo. Thus, the field of developmental biology is transitioning from microscopy to genome-wide chromatin descriptions. Ultimately, the prototype becomes a unique model for studying fundamental principles of development, epigenetic reprogramming, and cellular plasticity. In this review, we discuss chromatin reprogramming in the early mouse embryo, focusing on DNA methylation, chromatin accessibility, and higher-order chromatin structure.
© 2018 Ladstätter and Tachibana.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

