Histone supply: Multitiered regulation ensures chromatin dynamics throughout the cell cycle
- PMID: 30257851
- PMCID: PMC6314538
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201807179
Histone supply: Multitiered regulation ensures chromatin dynamics throughout the cell cycle
Abstract
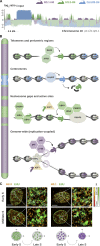
As the building blocks of chromatin, histones are central to establish and maintain particular chromatin states associated with given cell fates. Importantly, histones exist as distinct variants whose expression and incorporation into chromatin are tightly regulated during the cell cycle. During S phase, specialized replicative histone variants ensure the bulk of the chromatinization of the duplicating genome. Other non-replicative histone variants deposited throughout the cell cycle at specific loci use pathways uncoupled from DNA synthesis. Here, we review the particular dynamics of expression, cellular transit, assembly, and disassembly of replicative and non-replicative forms of the histone H3. Beyond the role of histone variants in chromatin dynamics, we review our current knowledge concerning their distinct regulation to control their expression at different levels including transcription, posttranscriptional processing, and protein stability. In light of this unique regulation, we highlight situations where perturbations in histone balance may lead to cellular dysfunction and pathologies.
© 2018 Mendiratta et al.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

