Identification of Novel Natural Substrates of Fibroblast Activation Protein-alpha by Differential Degradomics and Proteomics
- PMID: 30257879
- PMCID: PMC6317473
- DOI: 10.1074/mcp.RA118.001046
Identification of Novel Natural Substrates of Fibroblast Activation Protein-alpha by Differential Degradomics and Proteomics
Abstract
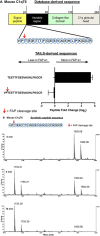
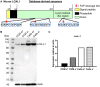
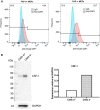
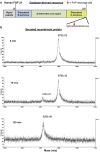
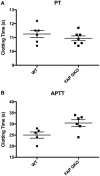
Fibroblast activation protein-alpha (FAP) is a cell-surface transmembrane-anchored dimeric protease. This unique, constitutively active serine protease has both dipeptidyl aminopeptidase and endopeptidase activities and can hydrolyze the post-proline bond. FAP expression is very low in adult organs but is upregulated by activated fibroblasts in sites of tissue remodeling, including fibrosis, atherosclerosis, arthritis and tumors. To identify the endogenous substrates of FAP, we immortalized primary mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) from FAP gene knockout embryos and then stably transduced them to express either enzymatically active or inactive FAP. The MEF secretomes were then analyzed using degradomic and proteomic techniques. Terminal amine isotopic labeling of substrates (TAILS)-based degradomics identified cleavage sites in collagens, many other extracellular matrix (ECM) and associated proteins, and lysyl oxidase-like-1, CXCL-5, CSF-1, and C1qT6, that were confirmed in vitro In addition, differential metabolic labeling coupled with quantitative proteomic analysis also implicated FAP in ECM-cell interactions, as well as with coagulation, metabolism and wound healing associated proteins. Plasma from FAP-deficient mice exhibited slower than wild-type clotting times. This study provides a significant expansion of the substrate repertoire of FAP and provides insight into the physiological and potential pathological roles of this enigmatic protease.
Keywords: Coagulation; Cytokines; Degradomics; Endopeptidases; Extracellular Matrix; Fibroblast Activation Protein; Fibroblasts; Proteases; SILAC; Substrate Identification.
© 2019 Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests
Figures




Similar articles
-
Increased expression of fibroblast activation protein-alpha in keloid fibroblasts: implications for development of a novel treatment option.Arch Dermatol Res. 2010 Dec;302(10):725-31. doi: 10.1007/s00403-010-1084-x. Epub 2010 Sep 26. Arch Dermatol Res. 2010. PMID: 20872224
-
Understanding fibroblast activation protein (FAP): substrates, activities, expression and targeting for cancer therapy.Proteomics Clin Appl. 2014 Jun;8(5-6):454-63. doi: 10.1002/prca.201300095. Epub 2014 Mar 24. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2014. PMID: 24470260 Review.
-
Fibroblast Activation Protein (FAP) Accelerates Collagen Degradation and Clearance from Lungs in Mice.J Biol Chem. 2016 Apr 8;291(15):8070-89. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.701433. Epub 2015 Dec 9. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26663085 Free PMC article.
-
A rare variant in human fibroblast activation protein associated with ER stress, loss of enzymatic function and loss of cell surface localisation.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Jul;1844(7):1248-59. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2014.03.015. Epub 2014 Apr 6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24717288
-
Fibroblast activation protein-α in fibrogenic disorders and cancer: more than a prolyl-specific peptidase?Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2017 Oct;21(10):977-991. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2017.1370455. Epub 2017 Aug 30. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2017. PMID: 28829211 Review.
Cited by
-
Overcoming stromal barriers to immuno-oncological responses via fibroblast activation protein-targeted therapy.Immunotherapy. 2021 Feb;13(2):155-175. doi: 10.2217/imt-2020-0066. Epub 2020 Nov 5. Immunotherapy. 2021. PMID: 33148078 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial, pericyte and tumor cell expression in glioblastoma identifies fibroblast activation protein (FAP) as an excellent target for immunotherapy.Clin Transl Immunology. 2020 Oct 14;9(10):e1191. doi: 10.1002/cti2.1191. eCollection 2020. Clin Transl Immunology. 2020. PMID: 33082953 Free PMC article.
-
Progressive changes in the protein expression profile of alveolar septa in early-stage lung adenocarcinoma.Int J Clin Oncol. 2024 Jun;29(6):771-779. doi: 10.1007/s10147-024-02507-1. Epub 2024 Apr 11. Int J Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38600426
-
CCL2: An Important Mediator Between Tumor Cells and Host Cells in Tumor Microenvironment.Front Oncol. 2021 Jul 27;11:722916. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.722916. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34386431 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The secreted inhibitor of invasive cell growth CREG1 is negatively regulated by cathepsin proteases.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Jan;78(2):733-755. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03528-5. Epub 2020 May 8. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 32385587 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Park J. E., Lenter M. C., Zimmermann R. N., Garin-Chesa P., Old L. J., and Rettig W. J. (1999) Fibroblast activation protein: A dual-specificity serine protease expressed in reactive human tumor stromal fibroblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 36505–36512 - PubMed
-
- Aertgeerts K., Levin I., Shi L., Snell G. P., Jennings A., Prasad G. S., Zhang Y., Kraus M. L., Salakian S., Sridhar V., Wijnands R., and Tennant M. G. (2005) Structural and kinetic analysis of the substrate specificity of human fibroblast activation protein {alpha}. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 19441–19444 - PubMed
-
- Lee K. N., Jackson K. W., Christiansen V. J., Lee C. S., Chun J. G., and McKee P. A. (2006) Antiplasmin-cleaving enzyme is a soluble form of fibroblast activation protein. Blood 107, 1397–1404 - PubMed
-
- Hamson E. J., Keane F. M., Tholen S., Schilling O., and Gorrell M. D. (2014) Understanding Fibroblast Activation Protein (FAP): substrates, activities, expression and targeting for cancer therapy. Proteomics Clin. Appl. 8, 454–463 - PubMed
-
- Polak N., and Gorrell M. D. (2018) Fibroblast activation protein; FAP. In: Choi S., ed. Encyclopedia of Signaling Molecules, 2nd Ed., pp. 1676–1681, Springer International Publishing, Cham
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

