TGFβ1 Cell Cycle Arrest Is Mediated by Inhibition of MCM Assembly in Rb-Deficient Conditions
- PMID: 30257992
- PMCID: PMC6318023
- DOI: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-18-0558
TGFβ1 Cell Cycle Arrest Is Mediated by Inhibition of MCM Assembly in Rb-Deficient Conditions
Abstract
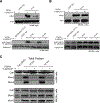
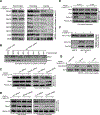
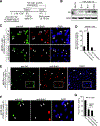
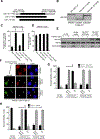
Transforming growth factor β1 (TGFβ1) is a potent inhibitor of cell growth that targets gene-regulatory events, but also inhibits the function of CDC45-MCM-GINS helicases (CMG; MCM, Mini-Chromosome Maintenance; GINS, Go-Ichi-Ni-San) through multiple mechanisms to achieve cell-cycle arrest. Early in G1, TGFβ1 blocks MCM subunit expression and suppresses Myc and Cyclin E/Cdk2 activity required for CMG assembly, should MCMs be expressed. Once CMGs are assembled in late-G1, TGFβ1 blocks CMG activation using a direct mechanism involving the retinoblastoma (Rb) tumor suppressor. Here, in cells lacking Rb, TGFβ1 does not suppress Myc, Cyclin E/Cdk2 activity, or MCM expression, yet growth arrest remains intact and Smad2/3/4-dependent. Such arrest occurs due to inhibition of MCM hexamer assembly by TGFβ1, which is not seen when Rb is present and MCM subunit expression is normally blocked by TGFβ1. Loss of Smad expression prevents TGFβ1 suppression of MCM assembly. Mechanistically, TGFβ1 blocks a Cyclin E-Mcm7 molecular interaction required for MCM hexamer assembly upstream of CDC10-dependent transcript-1 (CDT1) function. Accordingly, overexpression of CDT1 with an intact MCM-binding domain abrogates TGFβ1 arrest and rescues MCM assembly. The ability of CDT1 to restore MCM assembly and allow S-phase entry indicates that, in the absence of Rb and other canonical mediators, TGFβ1 relies on inhibition of Cyclin E-MCM7 and MCM assembly to achieve cell cycle arrest. IMPLICATIONS: These results demonstrate that the MCM assembly process is a pivotal target of TGFβ1 in eliciting cell cycle arrest, and provide evidence for a novel oncogenic role for CDT1 in abrogating TGFβ1 inhibition of MCM assembly.
©2018 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no financial or other conflicts of interest
Figures

Similar articles
-
The CMG helicase and cancer: a tumor "engine" and weakness with missing mutations.Oncogene. 2023 Feb;42(7):473-490. doi: 10.1038/s41388-022-02572-8. Epub 2022 Dec 15. Oncogene. 2023. PMID: 36522488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell cycle arrest by transforming growth factor beta1 near G1/S is mediated by acute abrogation of prereplication complex activation involving an Rb-MCM interaction.Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Feb;30(3):845-56. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01152-09. Epub 2009 Nov 30. Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 19948884 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of human minichromosome maintenance protein-binding protein with minichromosome maintenance 2-7.FEBS J. 2014 Feb;281(4):1057-67. doi: 10.1111/febs.12668. Epub 2014 Jan 15. FEBS J. 2014. PMID: 24299456
-
Mammalian MCM loading in late-G(1) coincides with Rb hyperphosphorylation and the transition to post-transcriptional control of progression into S-phase.PLoS One. 2009;4(5):e5462. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005462. Epub 2009 May 7. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19421323 Free PMC article.
-
Cell cycle and transcriptional control of human myeloid leukemic cells by transforming growth factor beta.Leuk Lymphoma. 2000 Jul;38(3-4):235-46. doi: 10.3109/10428190009087015. Leuk Lymphoma. 2000. PMID: 10830731 Review.
Cited by
-
The CMG helicase and cancer: a tumor "engine" and weakness with missing mutations.Oncogene. 2023 Feb;42(7):473-490. doi: 10.1038/s41388-022-02572-8. Epub 2022 Dec 15. Oncogene. 2023. PMID: 36522488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oridonin suppresses gastric cancer SGC-7901 cell proliferation by targeting the TNF-alpha/androgen receptor/TGF-beta signalling pathway axis.J Cell Mol Med. 2023 Sep;27(18):2661-2674. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17841. Epub 2023 Jul 11. J Cell Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37431884 Free PMC article.
-
NR4A1 knockdown confers hepatoprotection against ischaemia-reperfusion injury by suppressing TGFβ1 via inhibition of CYR61/NF-κB in mouse hepatocytes.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Jun;25(11):5099-5112. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16493. Epub 2021 May 3. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 33942481 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression profile analysis of severe influenza-based modulation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Oct 18;29(1):501. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-02107-9. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 39420432 Free PMC article.
-
Unwinding Helicase MCM Functionality for Diagnosis and Therapeutics of Replication Abnormalities Associated with Cancer: A Review.Mol Diagn Ther. 2024 May;28(3):249-264. doi: 10.1007/s40291-024-00701-5. Epub 2024 Mar 26. Mol Diagn Ther. 2024. PMID: 38530633 Review.
References
-
- Miyazawa K, Shinozaki M, Hara T, Furuya T, Miyazono K. Two major Smad pathways in TGF-beta superfamily signalling. Genes Cells. 2002;7(12):1191–204. - PubMed
-
- Hill CS. The Smads. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1999;31(11):1249–54. - PubMed
-
- Seoane J, Pouponnot C, Staller P, Schader M, Eilers M, Massague J. TGFbeta influences Myc, Miz-1 and Smad to control the CDK inhibitor p15INK4b. Nat Cell Biol. 2001;3(4):400–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

