Investigation of Endothelial Surface Glycocalyx Components and Ultrastructure by Single Molecule Localization Microscopy: Stochastic Optical Reconstruction Microscopy (STORM)
- PMID: 30258313
- PMCID: PMC6153618
Investigation of Endothelial Surface Glycocalyx Components and Ultrastructure by Single Molecule Localization Microscopy: Stochastic Optical Reconstruction Microscopy (STORM)
Abstract
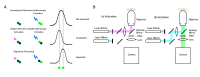
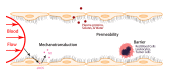
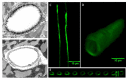
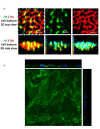
On the luminal surface of our blood vessels, there is a thin layer called endothelial surface glycocalyx (ESG) which consists of proteoglycans, glycosaminoglycans (GAGs), and glycoproteins. The GAGs in the ESG are heparan sulfate (HS), hyaluronic acid (HA), chondroitin sulfate (CS), and sialic acid (SA). In order to play important roles in regulating vascular functions, such as being a mechanosensor and transducer for the endothelial cells (ECs) to sense the blood flow, a molecular sieve to maintain normal microvessel permeability and a barrier between the circulating cells and endothelial cells forming the vessel wall, the ESG should have an organized structure at the molecular level. Due to the limitations of conventional optical and electrical microscopy, the ultrastructure of ESG, in the order of 10 to 100 nanometers, has not been revealed until recent development of a super resolution fluorescence optical microscope, Stochastic Optical Reconstruction Microscope (STORM), which is one type of single molecule localization microscopy. This short review describes how the STORM can overcome the diffraction barrier in the conventional fluorescence microscopy to identify the chemical components of the ESG at a high spatial resolution. Examples of the organized ultrastructure of the ESG on the in vitro EC monolayer revealed by the Nikon-STORM system are given as well as how its components get lost during the onset of sepsis, a systemic inflammatory syndrome induced by bacterial infection, which demonstrate that this new technique can be applied to discover the structural and molecular mechanisms at nanometer scales in the native cellular environment for the cellular functions under normal and disease conditions.
Keywords: Endothelial surface glycocalyx; Heparan sulfate; Hyaluronic acid; STORM; Ultrastructure.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endothelial surface glycocalyx (ESG) components and ultra-structure revealed by stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (STORM).Biorheology. 2019;56(2-3):77-88. doi: 10.3233/BIR-180204. Biorheology. 2019. PMID: 31045510
-
The structural stability of the endothelial glycocalyx after enzymatic removal of glycosaminoglycans.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e43168. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043168. Epub 2012 Aug 14. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22905223 Free PMC article.
-
Mechano-sensing and transduction by endothelial surface glycocalyx: composition, structure, and function.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2013 May-Jun;5(3):381-90. doi: 10.1002/wsbm.1211. Epub 2013 Feb 7. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2013. PMID: 23401243 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Endothelial Surface Glycocalyx in Mechanosensing and Transduction.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1097:1-27. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-96445-4_1. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 30315537 Review.
-
Endothelial Glycocalyx Impairment in Disease: Focus on Hyaluronan Shedding.Am J Pathol. 2020 Apr;190(4):768-780. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2019.11.016. Epub 2020 Feb 6. Am J Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32035885 Review.
Cited by
-
Cell-cell contact landscapes in Xenopus gastrula tissues.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Sep 28;118(39):e2107953118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2107953118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34544871 Free PMC article.
-
The Glycocalyx and Its Role in Vascular Physiology and Vascular Related Diseases.Cardiovasc Eng Technol. 2021 Feb;12(1):37-71. doi: 10.1007/s13239-020-00485-9. Epub 2020 Sep 21. Cardiovasc Eng Technol. 2021. PMID: 32959164 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Density Distribution Maps: A Novel Tool for Subcellular Distribution Analysis and Quantitative Biomedical Imaging.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Feb 2;21(3):1009. doi: 10.3390/s21031009. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33540807 Free PMC article.
-
Scanning Probe Microscopy Techniques for Studying the Cell Glycocalyx.Cells. 2023 Dec 6;12(24):2778. doi: 10.3390/cells12242778. Cells. 2023. PMID: 38132098 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Heparin and Glycocalyx in Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 21;12:754141. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.754141. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34992593 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abbe E. Beiträge zur Theorie des Mikroskops und der mikroskopischen Wahrnehmung. Archiv für mikroskopische Anatomie. 1873;9(1):413-8.
-
- Tarbell JM, Ebong EE. The endothelial glycocalyx: a mechano-sensor and-transducer [-pt.] Sci Signal. 2008;1(40):pt8. - PubMed
-
- Tarbell JM, Pahakis MY. Mechanotransduction and the glycocalyx. J Intern Med. 2006;259(4):339–50. - PubMed
-
- Hell SW, Wichmann J. Breaking the diffraction resolution limit by stimulated emission: stimulated-emission-depletion fluorescence microscopy. Opt Lett. 1994;19(11):780–2. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
