Pierce's Disease of Grapevines: A Review of Control Strategies and an Outline of an Epidemiological Model
- PMID: 30258423
- PMCID: PMC6143690
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02141
Pierce's Disease of Grapevines: A Review of Control Strategies and an Outline of an Epidemiological Model
Abstract
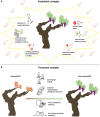
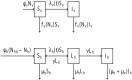
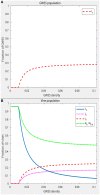
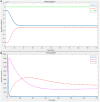
Xylella fastidiosa is a notorious plant pathogenic bacterium that represents a threat to crops worldwide. Its subspecies, Xylella fastidiosa subsp. fastidiosa is the causal agent of Pierce's disease of grapevines. Pierce's disease has presented a serious challenge for the grapevine industry in the United States and turned into an epidemic in Southern California due to the invasion of the insect vector Homalodisca vitripennis. In an attempt to minimize the effects of Xylella fastidiosa subsp. fastidiosa in vineyards, various studies have been developing and testing strategies to prevent the occurrence of Pierce's disease, i.e., prophylactic strategies. Research has also been undertaken to investigate therapeutic strategies to cure vines infected by Xylella fastidiosa subsp. fastidiosa. This report explicitly reviews all the strategies published to date and specifies their current status. Furthermore, an epidemiological model of Xylella fastidiosa subsp. fastidiosa is proposed and key parameters for the spread of Pierce's disease deciphered in a sensitivity analysis of all model parameters. Based on these results, it is concluded that future studies should prioritize therapeutic strategies, while investments should only be made in prophylactic strategies that have demonstrated promising results in vineyards.
Keywords: Homalodisca vitripennis; Pierce's disease; Xylella fastidiosa; control strategies; epidemiological model; grapevine; prophylactic; therapeutic.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lessons from One Fastidious Bacterium to Another: What Can We Learn about Liberibacter Species from Xylella fastidiosa.Insects. 2019 Sep 16;10(9):300. doi: 10.3390/insects10090300. Insects. 2019. PMID: 31527458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Models Applied to Grapevine Pests: A Review.Insects. 2021 Feb 16;12(2):169. doi: 10.3390/insects12020169. Insects. 2021. PMID: 33669418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Detection and analysis of the bacterium, Xylella fastidiosa, in glassy-winged sharpshooter, Homalodisca vitripennis, populations in Texas.J Insect Sci. 2010;10:168. doi: 10.1673/031.010.14128. J Insect Sci. 2010. PMID: 21062210 Free PMC article.
-
Xylella fastidiosa and Glassy-Winged Sharpshooter Population Dynamics in the Southern San Joaquin Valley of California.Plant Dis. 2020 Nov;104(11):2994-3001. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-01-20-0066-RE. Epub 2020 Aug 27. Plant Dis. 2020. PMID: 32852243
-
Citrus and Coffee Strains of Xylella fastidiosa Induce Pierce's Disease in Grapevine.Plant Dis. 2002 Nov;86(11):1206-1210. doi: 10.1094/PDIS.2002.86.11.1206. Plant Dis. 2002. PMID: 30818468
Cited by
-
Lessons from One Fastidious Bacterium to Another: What Can We Learn about Liberibacter Species from Xylella fastidiosa.Insects. 2019 Sep 16;10(9):300. doi: 10.3390/insects10090300. Insects. 2019. PMID: 31527458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated targeted mutagenesis of TAS4 and MYBA7 loci in grapevine rootstock 101-14.Transgenic Res. 2020 Jun;29(3):355-367. doi: 10.1007/s11248-020-00196-w. Epub 2020 Apr 23. Transgenic Res. 2020. PMID: 32328868 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond Risk: Bacterial Biofilms and Their Regulating Approaches.Front Microbiol. 2020 May 21;11:928. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00928. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32508772 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Models Applied to Grapevine Pests: A Review.Insects. 2021 Feb 16;12(2):169. doi: 10.3390/insects12020169. Insects. 2021. PMID: 33669418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Xylella fastidiosa subspecies pauca in European olives.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Apr 28;117(17):9250-9259. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1912206117. Epub 2020 Apr 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32284411 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agüero C. B., Uratsu S. L., Greve C., Powell A. L., Labavitch J. M., Meredith C. P., et al. . (2005). Evaluation of tolerance to Pierce's disease and Botrytis in transgenic plants of Vitis vinifera L. expressing the pear PGIP gene. Mol. Plant Pathol. 6, 43–51. 10.1111/j.1364-3703.2004.00262.x - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

