Prophylactic Zinc and Therapeutic Selenium Administration Increases the Antioxidant Enzyme Activity in the Rat Temporoparietal Cortex and Improves Memory after a Transient Hypoxia-Ischemia
- PMID: 30258527
- PMCID: PMC6146673
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/9416432
Prophylactic Zinc and Therapeutic Selenium Administration Increases the Antioxidant Enzyme Activity in the Rat Temporoparietal Cortex and Improves Memory after a Transient Hypoxia-Ischemia
Abstract
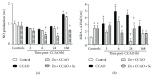
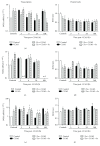
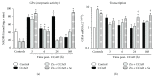
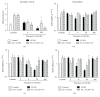
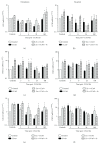
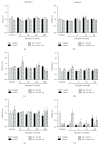
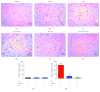
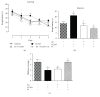
In the cerebral hypoxia-ischemia rat model, the prophylactic administration of zinc can cause either cytotoxicity or preconditioning effect, whereas the therapeutic administration of selenium decreases the ischemic damage. Herein, we aimed to explore whether supplementation of low doses of prophylactic zinc and therapeutic selenium could protect from a transient hypoxic-ischemic event. We administrated zinc (0.2 mg/kg of body weight; ip) daily for 14 days before a 10 min common carotid artery occlusion (CCAO). After CCAO, we administrated sodium selenite (6 μg/kg of body weight; ip) daily for 7 days. In the temporoparietal cerebral cortex, we determined nitrites by the Griess method and lipid peroxidation by the Gerard-Monnier assay. qPCR was used to measure mRNA of nitric oxide synthases, antioxidant enzymes, chemokines, and their receptors. We measured the enzymatic activity of SOD and GPx and protein levels of chemokines and their receptors by ELISA. We evaluated long-term memory using the Morris-Water maze test. Our results showed that prophylactic administration of zinc caused a preconditioning effect, decreasing nitrosative/oxidative stress and increasing GPx and SOD expression and activity, as well as eNOS expression. The therapeutic administration of selenium maintained this preconditioning effect up to the late phase of hypoxia-ischemia. Ccl2, Ccr2, Cxcl12, and Cxcr4 were upregulated, and long-term memory was improved. Pyknotic cells were decreased suggesting prevention of neuronal cell death. Our results show that the prophylactic zinc and therapeutic selenium administration induces effective neuroprotection in the early and late phases after CCAO.
Figures
References
-
- Blanco-Alvarez V. M., Soto-Rodriguez G., Gonzalez-Barrios J. A., et al. Prophylactic subacute administration of zinc increases CCL2, CCR2, FGF2, and IGF-1 expression and prevents the long-term memory loss in a rat model of cerebral hypoxia-ischemia. Neural Plasticity. 2015;2015:15. doi: 10.1155/2015/375391.375391 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

