High speed visual stimuli generator to estimate the minimum presentation time required for an orientation discrimination task
- PMID: 30258679
- PMCID: PMC6154181
- DOI: 10.1364/BOE.9.002640
High speed visual stimuli generator to estimate the minimum presentation time required for an orientation discrimination task
Abstract
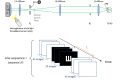
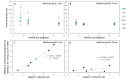
How brief can a visual stimulus be and still be seen? To answer this question, we developed a digital micromirror device (DMD) based system operating at high speed (22.7 kHz) to control the rapid presentation of visual stimuli and estimated the minimum time required to identify the orientation of tumbling Snellen E letters. Time thresholds were measured in five subjects using a QUEST algorithm to vary the presentation time of the letters subtending either 0.75°, 1.5° and 4.5° on the retina, for two different effective pupil sizes (0.3 and 1 mm). Additionally, to evaluate the effect of defocus on time thresholds, the experiment was repeated with 1.5° letters and induced myopic defocus with 3, 6 and 9 D trial lenses placed in a conjugated pupil plane. We found that subjects were able to identify the orientation of the letters presented as briefly as 5 ms.
Keywords: (230.0230) Optical devices; (230.3990) Micro-optical devices; (230.6120) Spatial light modulators; (330.0330) Vision, color, and visual optics; (330.5510) Psychophysics; (330.6790) Temporal discrimination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest related to this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Spherical Equivalent.2023 May 11. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2023 May 11. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36943975 Free Books & Documents.
-
Defocus blur discrimination in natural images with natural optics.J Vis. 2015;15(5):16. doi: 10.1167/15.5.16. J Vis. 2015. PMID: 26067534 Free PMC article.
-
Analysing the impact of myopia on the Stiles-Crawford effect of the first kind using a digital micromirror device.Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2018 May;38(3):273-280. doi: 10.1111/opo.12441. Epub 2018 Jan 30. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2018. PMID: 29380408
-
Temporal integration of visual signals in lens compensation (a review).Exp Eye Res. 2013 Sep;114:69-76. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2013.02.014. Epub 2013 Mar 5. Exp Eye Res. 2013. PMID: 23470505 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Astigmatic Peripheral Defocus with Different Contact Lenses: Review and Meta-Analysis.Curr Eye Res. 2016 Aug;41(8):1005-1015. doi: 10.3109/02713683.2015.1116585. Epub 2016 Feb 2. Curr Eye Res. 2016. PMID: 26835871 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the correlation and causation between alpha oscillations and one-second time perception through EEG and tACS.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 5;14(1):8035. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-57715-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38580671 Free PMC article.
-
Contrast sensitivity is resilient to induced fast periodic defocus oscillations.Biomed Opt Express. 2024 May 20;15(6):3848-3858. doi: 10.1364/BOE.521340. eCollection 2024 Jun 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2024. PMID: 38867768 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
