Methotrexate Cutaneous Toxicity following a Single Dose of 10 mg in a Case of Chronic Plaque Psoriasis: A Possible Idiosyncratic Reaction
- PMID: 30258802
- PMCID: PMC6137652
- DOI: 10.4103/idoj.IDOJ_316_17
Methotrexate Cutaneous Toxicity following a Single Dose of 10 mg in a Case of Chronic Plaque Psoriasis: A Possible Idiosyncratic Reaction
Abstract
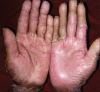
Low-dose methotrexate is a well-tolerated and inexpensive systemic immunosuppressive agent used commonly in dermatology. However, several adverse events such as pancytopenia, pneumonitis, mucositis, and cutaneous ulcerations may develop during acute toxicity with dose-dependent or idiosyncratic mechanisms. Risk factors for methotrexate toxicity include advanced age, hypoalbuminemia, renal dysfunction, and concomitant drugs increasing the level of methotrexate in the body. We present a case of methotrexate toxicity presenting with classical features along with mucocutaneous side-effects, such as ulceration of psoriatic plaques and acral erythema, following a single dose of methotrexate.
Keywords: Cutaneous ulceration; low-dose methotrexate; methotrexate toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Naranjo CA, Busto U, Sellers EM, Sandor P, Ruiz I, Roberts EA, et al. A method for estimating the probability of adverse drug reactions. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1981;30:239–45. - PubMed
-
- The use of the WHO-UMC system for standardised case causality assessment. [Last accessed on 2018 Jan 29]. Available from: http://www.WHO-UMC.org/graphics/4409.pdf .
-
- Agarwal V, Chauhan S, Singh R, Sachdev A, D'Cruz S, Tahlan A. Pancytopenia with the first dose of methotrexate in a patient with psoriatic arthritis. J Indian Rheumatol Assoc. 2005;13:60–1.

