Epithelial protein lost in neoplasm (EPLIN): Beyond a tumor suppressor
- PMID: 30258911
- PMCID: PMC6136588
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gendis.2017.03.002
Epithelial protein lost in neoplasm (EPLIN): Beyond a tumor suppressor
Abstract
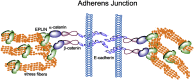
The majority of cancer-related deaths are caused by tumor recurrence, metastasis and therapeutic resistance. During the late stages of tumor progression, multiple factors are involved, including the downregulation and/or loss of function of metastasis suppressors. Epithelial protein lost in neoplasm (EPLIN), an actin-binding protein, was initially identified as a putative tumor suppressor that is frequently downregulated in epithelial tumors. Recent evidence indicates that EPLIN may negatively regulate epithelia-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), a crucial process by which cancer cells acquire invasive capabilities and therapeutic resistance. Importantly, downregulation of EPLIN is associated with clinical metastasis in a variety of solid tumors, suggesting that EPLIN could be a suppressor of metastasis. In this review, I will discuss the regulation and function of EPLIN in human cancer cells and explore the clinical significance of EPLIN in metastatic disease.
Keywords: Actin cytoskeleton; Chemoresistance; EPLIN; Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition; Metastasis suppressor; Tumor suppressor.
Figures

Similar articles
-
EPLIN downregulation promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer cells and correlates with clinical lymph node metastasis.Oncogene. 2011 Dec 15;30(50):4941-52. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.199. Epub 2011 May 30. Oncogene. 2011. PMID: 21625216 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal growth factor promotes protein degradation of epithelial protein lost in neoplasm (EPLIN), a putative metastasis suppressor, during epithelial-mesenchymal transition.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jan 18;288(3):1469-79. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.438341. Epub 2012 Nov 27. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23188829 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial protein lost in neoplasm (EPLIN) and prostate cancer: lessons learned from the ARCaP model.Am J Clin Exp Urol. 2021 Aug 25;9(4):264-276. eCollection 2021. Am J Clin Exp Urol. 2021. PMID: 34541025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EPLIN: a fundamental actin regulator in cancer metastasis?Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2015 Dec;34(4):753-64. doi: 10.1007/s10555-015-9595-8. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2015. PMID: 26350886 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epithelial protein lost in neoplasm-α (EPLIN-α) is a potential prognostic marker for the progression of epithelial ovarian cancer.Int J Oncol. 2016 Jun;48(6):2488-96. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2016.3462. Epub 2016 Mar 29. Int J Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27035883
Cited by
-
Epithelial Protein Lost in Neoplasm, EPLIN, the Cellular and Molecular Prospects in Cancers.Biomolecules. 2021 Jul 16;11(7):1038. doi: 10.3390/biom11071038. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34356662 Free PMC article. Review.
-
UBXN2A suppresses the Rictor-mTORC2 signaling pathway, an established tumorigenic pathway in human colorectal cancer.Oncogene. 2023 May;42(21):1763-1776. doi: 10.1038/s41388-023-02686-7. Epub 2023 Apr 10. Oncogene. 2023. PMID: 37037900 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and molecular insights of lima1 in cholangiocarcinoma.Cell Adh Migr. 2024 Dec;18(1):4-17. doi: 10.1080/19336918.2024.2383068. Epub 2024 Jul 30. Cell Adh Migr. 2024. PMID: 39076043 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of LIMA1 Indicates Poor Prognosis and Promotes Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Clin Med Insights Oncol. 2022 Jul 8;16:11795549221109493. doi: 10.1177/11795549221109493. eCollection 2022. Clin Med Insights Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35837368 Free PMC article.
-
Rab40-Cullin5 complex regulates EPLIN and actin cytoskeleton dynamics during cell migration.J Cell Biol. 2021 Jul 5;220(7):e202008060. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202008060. Epub 2021 May 17. J Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 33999101 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Buchanan C., Lago Huvelle M.A., Peters M.G. Metastasis suppressors: basic and translational advances. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2011;12(11):1948–1960. - PubMed
-
- Fatemian T., Chowdhury E.H. Targeting oncogenes and tumor suppressors genes to mitigate chemoresistance. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2014;14(7):599–609. - PubMed
-
- Oren M. Tumor suppressors. Teaming up to restrain cancer. Nature. 1998;391(6664):233–234. - PubMed
-
- Steeg P.S. Metastasis suppressors alter the signal transduction of cancer cells. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3(1):55–63. - PubMed
-
- Thiolloy S., Rinker-Schaeffer C.W. Thinking outside the box: using metastasis suppressors as molecular tools. Semin Cancer Biol. 2011;21(2):89–98. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

