A Possible Link Between HCN Channels and Depression
- PMID: 30259006
- PMCID: PMC6152912
- DOI: 10.1177/2470547018787781
A Possible Link Between HCN Channels and Depression
Abstract
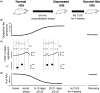
Growing evidence suggests a possible link between hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated nonselective cation (HCN) channels and depression. In a recent study published in Molecular Psychiatry, we first demonstrate that I h (the membrane current mediated by HCN channels) and HCN1 protein expression were increased in dorsal, but not in ventral, CA1 region following chronic, but not acute stress. This upregulation of I h was restricted to the perisomatic region of CA1 neurons and contributed to a reduction of neuronal excitability. A reduction of HCN1 protein expression in dorsal CA1 region before the onset of chronic unpredictable stress-induced depression was sufficient to provide resilient effects to chronic unpredictable stress. Furthermore, in vivo block of the sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA) pumps, a manipulation known to increase intracellular calcium levels and upregulate I h, produced anxiogenic-like behavior and an increase in I h, similar to that observed in chronic unpredictable stress model of depression. Here, we share our view on (1) how the function and expression of HCN1 channels are changed in the brain in a subcellular region-specific manner during the development of depression and (2) how a reduction of HCN1 protein expression provides resilience to chronic stress.
Keywords: HCN1; Ih; chronic unpredictable stress; hippocampus; resilience.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interests with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

Comment on
-
Perisomatic changes in h-channels regulate depressive behaviors following chronic unpredictable stress.Mol Psychiatry. 2018 Apr;23(4):892-903. doi: 10.1038/mp.2017.28. Epub 2017 Apr 18. Mol Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 28416809 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Perisomatic changes in h-channels regulate depressive behaviors following chronic unpredictable stress.Mol Psychiatry. 2018 Apr;23(4):892-903. doi: 10.1038/mp.2017.28. Epub 2017 Apr 18. Mol Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 28416809 Free PMC article.
-
Glucocorticoid-glucocorticoid receptor-HCN1 channels reduce neuronal excitability in dorsal hippocampal CA1 neurons.Mol Psychiatry. 2022 Oct;27(10):4035-4049. doi: 10.1038/s41380-022-01682-9. Epub 2022 Jul 15. Mol Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35840797 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of hyperpolarization-activated, cyclic nucleotide-gated cation channels in dorsal root ganglion in neuropathic pain.Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2008 Oct 25;60(5):579-80. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2008. PMID: 18958363
-
Neurophysiology of HCN channels: from cellular functions to multiple regulations.Prog Neurobiol. 2014 Jan;112:1-23. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.10.001. Epub 2013 Oct 29. Prog Neurobiol. 2014. PMID: 24184323 Review.
-
HCN channels as targets for drug discovery.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2009 Jan;12(1):64-72. doi: 10.2174/138620709787048028. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2009. PMID: 19149492 Review.
Cited by
-
Missing Puzzle Pieces in Dementia Research: HCN Channels and Theta Oscillations.Aging Dis. 2024 Feb 1;15(1):22-42. doi: 10.14336/AD.2023.0607. Aging Dis. 2024. PMID: 37450922 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Integrative Approach to Ketamine Therapy May Enhance Multiple Dimensions of Efficacy: Improving Therapeutic Outcomes With Treatment Resistant Depression.Front Psychiatry. 2021 Nov 24;12:710338. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.710338. eCollection 2021. Front Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34899408 Free PMC article.
-
Alteration of hyperpolarization-activated cation current-mediated metaplasticity contributes to electroconvulsive shock-induced learning and memory impairment in depressed rats.Front Psychiatry. 2024 Jun 7;15:1365119. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1365119. eCollection 2024. Front Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38911706 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal Methyl-Enriched Diet Increases DNMT1, HCN1, and TH Gene Expression and Suppresses Absence Seizures and Comorbid Depression in Offspring of WAG/Rij Rats.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Jan 21;13(3):398. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13030398. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36766503 Free PMC article.
-
Antidepressant Effects of (S)-Ketamine through a Reduction of Hyperpolarization-Activated Current Ih.iScience. 2020 Jun 26;23(6):101239. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.101239. Epub 2020 Jun 4. iScience. 2020. PMID: 32629607 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mayberg HS. Limbic-cortical dysregulation: a proposed model of depression. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 1997; 9: 471–481. - PubMed
-
- Mayberg HS, Brannan SK, Tekell JL, et al. Regional metabolic effects of fluoxetine in major depression: serial changes and relationship to clinical response. Biol Psychiatry. 2000; 48: 830–843. - PubMed
-
- Fava M. Diagnosis and definition of treatment-resistant depression. Biol Psychiatry. 2003; 53: 649–659. - PubMed
-
- Mayberg HS, Lozano AM, Voon V, et al. Deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression. Neuron. 2005; 45: 651–660. - PubMed
-
- Berman RM, Cappiello A, Anand A, et al. Antidepressant effects of ketamine in depressed patients. Biol Psychiatry. 2000; 47: 351–354. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

