Prefrontal circuits signaling active avoidance retrieval and extinction
- PMID: 30259076
- PMCID: PMC6461357
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-018-5012-7
Prefrontal circuits signaling active avoidance retrieval and extinction
Abstract
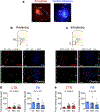
Objective: Neurons in PL and IL project densely to two areas implicated in active avoidance: the basolateral amygdala (BLA) and the ventral striatum (VS). We therefore combined c-Fos immunohistochemistry with retrograde tracers to characterize signaling in platform-mediated active avoidance.
Methods: Male rats were infused with retrograde tracers (CTB, FB) into basolateral amygdala and ventral striatum and conditioned to avoid tone-signaled footshocks by stepping onto a nearby platform. In a subsequent test session, rats received either 2 unreinforced tones (avoidance retrieval) or 15 unreinforced tones (avoidance extinction) followed by analysis of c-Fos combined with fluorescent imaging of retrograde tracers.
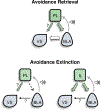
Results: Retrieval of avoidance did not activate IL neurons, but did activate PL neurons projecting to BLA, and to a lesser extent VS. Extinction of avoidance activated IL neurons projecting to both BLA and VS, as well as PL neurons projecting to VS.
Conclusions: Our observation that avoidance retrieval is signaled by PL projections to BLA suggests that PL may modulate VS indirectly via BLA, and agrees with other findings implicating BLA in active avoidance. Less expected was the signaling of extinction via PL inputs to VS, which may converge with IL inputs to VS to inhibit expression of avoidance.
Keywords: Amygdala; Infralimbic; Prelimbic; Retrograde tracers; Ventral striatum; c-Fos.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

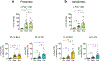
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

