Monoamine oxidase isoenzymes: genes, functions and targets for behavior and cancer therapy
- PMID: 30259128
- PMCID: PMC6245662
- DOI: 10.1007/s00702-018-1927-8
Monoamine oxidase isoenzymes: genes, functions and targets for behavior and cancer therapy
Abstract
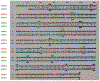
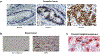
Monoamine oxidase (MAO) catalyzes the oxidative deamination of monoamine neurotransmitters and dietary amines. Two pharmacological types with different substrate and inhibitor specificities were reported. Molecular cloning revealed that the two types of MAO were different genes expressed as different proteins with different functions. MAO A and B have identical intron-exon organization derived by duplication of a common ancestral gene thus they are termed isoenzymes. MAO A knockout mice exhibited aggression, the first clear evidence linking genes to behavior. MAO A KO mice exhibited autistic-like behaviors which could be prevented by reducing serotonin levels at an early developmental age (P1-P7) providing potential therapy. MAO B KO mice were non-aggressive and resistant to Parkinsongenic neurotoxin. More recently it was found that MAO A is overexpressed in prostate cancer and correlates with degree of malignancy. The oncogenic mechanism involves a ROS-activated AKT/FOXO1/TWIST1 signaling pathway. Deletion of MAO A reduced prostate cancer stem cells and suppressed invasive adenocarcinoma. MAO A was also overexpressed in classical Hodgkin lymphoma and glioma brain tumors. MAO B was overexpressed in glioma and non-small cell lung cancer. MAO A inhibitors reduce the growth of prostate cancer, drug sensitive and resistant gliomas and classical Hodgkin lymphoma, and enhance standard chemotherapy. Currently, we are developing NIR dye-conjugated clorgyline (MAO A inhibitor) as a novel dual therapeutic/diagnostic agent for cancer. A phase II clinical trial of MAO inhibitor for biochemical recurrent prostate cancer is ongoing. The role of MAO A and B in several cancer types opens new avenues for cancer therapies.
Keywords: Autism; Behavior; Cancer; Gene; Isoenzyme; Metastasis; Monoamine oxidase; Survival; Therapy.
Figures
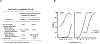
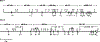




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

