Tight junction structure, function, and assessment in the critically ill: a systematic review
- PMID: 30259344
- PMCID: PMC6158145
- DOI: 10.1186/s40635-018-0203-4
Tight junction structure, function, and assessment in the critically ill: a systematic review
Abstract
Background: Epithelial and endothelial barrier integrity, essential for homeostasis, is maintained by cellular boarder structures known as tight junctions (TJs). In critical illness, TJs may become disrupted, resulting in barrier dysfunction manifesting as capillary leak, pulmonary edema, gut bacterial translocation, and multiple organ failure. We aim to provide a clinically focused overview of TJ structure and function and systematically review and analyze all studies assessing markers of endothelial and epithelial TJ breakdown correlated with clinical outcomes in critically ill humans.
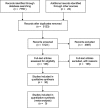
Methods: We systematically searched MEDLINE, EMBASE, and PubMed. Additional articles were identified by targeted searches. We included studies that looked at the relationship between biomarkers of endothelial or epithelial TJ structure or function and critical illness. Results were qualitatively analyzed due to sample size and heterogeneity.
Results: A total of 5297 abstracts met search criteria, of which 150 articles met requirements for full text review. Of these, 30 studies met inclusion criteria. Fifteen of the 30 reports investigated proteins of endothelial tight junctions and 15 investigated epithelial TJ markers, exclusively in the gastrointestinal epithelium. No studies investigated TJ-derived proteins in primary cardiac or pulmonary pathology.
Conclusions: TJ integrity is essential for homeostasis. We identified multiple studies that indicate TJs are disrupted by critical illness. These studies highlight the significance of barrier disruption across many critical disease states and correlate TJ-associated markers to clinically relevant outcomes. Further study on the role of multiple tissue-specific claudins, particularly in the setting of respiratory or cardiac failure, may lead to diagnostic and therapeutic advances.
Systematic review registration: This systematic review is registered in the PROSPERO database: CRD42017074546 .
Keywords: Capillary leak; Cellular permeability; Critical care; Endothelial cells; Epithelial cells; Tight junctions.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there are no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

References
-
- Tokes A-M, Schaff Z, Szasz AM, Kulka J. The distribution of tight junctions and junctional proteins in the human bodytight junctions in cancer metastasis. 2013. pp. 29–64.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

