A Connectomic Atlas of the Human Cerebrum-Chapter 9: The Occipital Lobe
- PMID: 30260435
- PMCID: PMC6888039
- DOI: 10.1093/ons/opy263
A Connectomic Atlas of the Human Cerebrum-Chapter 9: The Occipital Lobe
Abstract
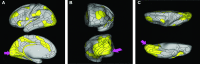
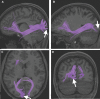
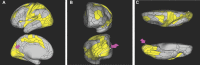
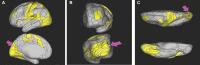
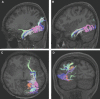
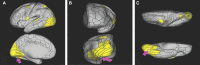
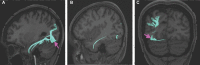
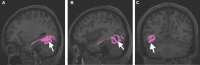
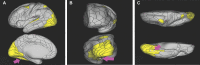
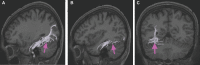
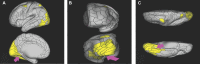
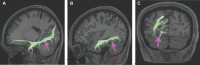
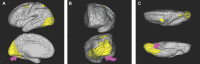
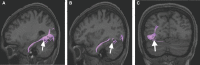
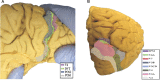
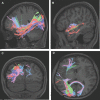
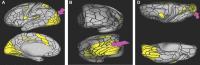
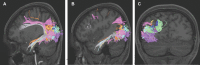
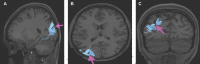
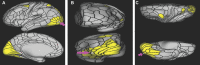
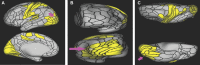
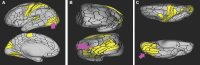
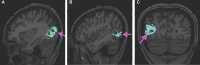
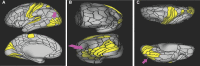
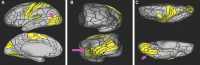
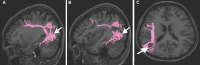
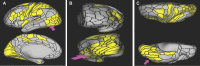
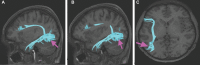
In this supplement, we build on work previously published under the Human Connectome Project. Specifically, we seek to show a comprehensive anatomic atlas of the human cerebrum demonstrating all 180 distinct regions comprising the cerebral cortex. The location, functional connectivity, and structural connectivity of these regions are outlined, and where possible a discussion is included of the functional significance of these areas. In part 9, we specifically address regions relevant to the occipital lobe and the visual system.
Figures














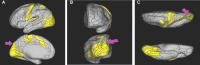
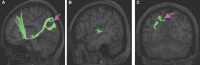
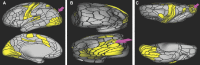


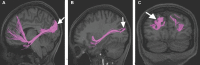










Similar articles
-
A Connectomic Atlas of the Human Cerebrum-Chapter 8: The Posterior Cingulate Cortex, Medial Parietal Lobe, and Parieto-Occipital Sulcus.Oper Neurosurg. 2018 Dec 1;15(suppl_1):S350-S371. doi: 10.1093/ons/opy262. Oper Neurosurg. 2018. PMID: 30260425 Free PMC article.
-
A Connectomic Atlas of the Human Cerebrum-Chapter 16: Tractographic Description of the Vertical Occipital Fasciculus.Oper Neurosurg. 2018 Dec 1;15(suppl_1):S456-S461. doi: 10.1093/ons/opy270. Oper Neurosurg. 2018. PMID: 30260427 Free PMC article.
-
A Connectomic Atlas of the Human Cerebrum-Chapter 6: The Temporal Lobe.Oper Neurosurg. 2018 Dec 1;15(suppl_1):S245-S294. doi: 10.1093/ons/opy260. Oper Neurosurg. 2018. PMID: 30260447 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging connectivity: MRI and the structural networks of the brain.Funct Neurol. 2013 Jul-Sep;28(3):197-203. Funct Neurol. 2013. PMID: 24139656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The anatomy of the human frontal lobe.Handb Clin Neurol. 2019;163:95-122. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-804281-6.00006-9. Handb Clin Neurol. 2019. PMID: 31590750 Review.
Cited by
-
The Changes of Brain Function After Spinal Manipulation Therapy in Patients with Chronic Low Back Pain: A Rest BOLD fMRI Study.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2022 Feb 5;18:187-199. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S339762. eCollection 2022. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2022. PMID: 35153482 Free PMC article.
-
Reducing the Cognitive Footprint of Brain Tumor Surgery.Front Neurol. 2021 Aug 16;12:711646. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.711646. eCollection 2021. Front Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34484105 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efferent compared to afferent neural substrates of the vergence eye movement system evoked via fMRI.Front Neurosci. 2025 Jan 8;18:1497326. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1497326. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 39844855 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in local brain function in mild cognitive impairment due to semantic dementia.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2021 May;27(5):587-602. doi: 10.1111/cns.13621. Epub 2021 Mar 2. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2021. PMID: 33650764 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation Between Neurocognitive Outcomes and Neuroaxonal Connectome Alterations After Whole Brain Radiotherapy: A Proof-of-Concept Study.Cancers (Basel). 2025 May 23;17(11):1752. doi: 10.3390/cancers17111752. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40507233 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wandell BA, Dumoulin SO, Brewer AA. Visual field maps in human cortex. Neuron. 2007;56(2):366-383. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

