A Connectomic Atlas of the Human Cerebrum-Chapter 12: Tractographic Description of the Middle Longitudinal Fasciculus
- PMID: 30260450
- PMCID: PMC6887674
- DOI: 10.1093/ons/opy266
A Connectomic Atlas of the Human Cerebrum-Chapter 12: Tractographic Description of the Middle Longitudinal Fasciculus
Abstract
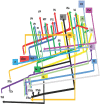
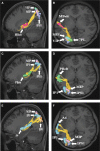
The middle longitudinal fasciculus (MdLF) is a small and somewhat controversial white matter tract of the human cerebrum, confined to the posterior superior temporal region from which it courses posteriorly to connect at the occipital-parietal interface. The tract appears to be involved in language processing as well as auditory organization and localization, while sub-serving other higher level cognitive functions that have yet to be fully elucidated. Little is known about the specific, interparcellation connections that integrate to form the MdLF. Utilizing diffusion spectrum magnetic resonance imaging tractography coupled with the human cortex parcellation data presented earlier in this supplement, we aim to describe the macro-connectome of the MdLF in relation to the linked parcellations present within the human cortex. The purpose of this study is to present this information in an indexed, illustrated, and tractographically aided series of figures and tables for anatomic and clinical reference.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A Connectomic Atlas of the Human Cerebrum-Chapter 10: Tractographic Description of the Superior Longitudinal Fasciculus.Oper Neurosurg. 2018 Dec 1;15(suppl_1):S407-S422. doi: 10.1093/ons/opy264. Oper Neurosurg. 2018. PMID: 30260421 Free PMC article.
-
A Connectomic Atlas of the Human Cerebrum-Chapter 13: Tractographic Description of the Inferior Fronto-Occipital Fasciculus.Oper Neurosurg. 2018 Dec 1;15(suppl_1):S436-S443. doi: 10.1093/ons/opy267. Oper Neurosurg. 2018. PMID: 30260438 Free PMC article.
-
A Connectomic Atlas of the Human Cerebrum-Chapter 11: Tractographic Description of the Inferior Longitudinal Fasciculus.Oper Neurosurg. 2018 Dec 1;15(suppl_1):S423-S428. doi: 10.1093/ons/opy265. Oper Neurosurg. 2018. PMID: 30260434 Free PMC article.
-
Anatomical variability of the arcuate fasciculus: a systematical review.Surg Radiol Anat. 2019 Aug;41(8):889-900. doi: 10.1007/s00276-019-02244-5. Epub 2019 Apr 26. Surg Radiol Anat. 2019. PMID: 31028450
-
The white matter architecture underlying semantic processing: A systematic review.Neuropsychologia. 2020 Jan;136:107182. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2019.107182. Epub 2019 Sep 27. Neuropsychologia. 2020. PMID: 31568774
Cited by
-
A narrative review of the anatomy and function of the white matter tracts in language production and comprehension.Front Hum Neurosci. 2023 Mar 27;17:1139292. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2023.1139292. eCollection 2023. Front Hum Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37051488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Frontal Aslant Tract and Supplementary Motor Area Syndrome: Moving towards a Connectomic Initiation Axis.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Mar 5;13(5):1116. doi: 10.3390/cancers13051116. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33807749 Free PMC article.
-
Networks for proper versus common name retrieval: insights from causal mapping and new hypotheses.Brain Commun. 2025 Jun 25;7(4):fcaf256. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcaf256. eCollection 2025. Brain Commun. 2025. PMID: 40661329 Free PMC article. Review.
-
White matter abnormalities in adults with bipolar disorder type-II and unipolar depression.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 6;11(1):7541. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-87069-2. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33824408 Free PMC article.
-
Simulating the impact of white matter connectivity on processing time scales using brain network models.Commun Biol. 2025 Feb 7;8(1):197. doi: 10.1038/s42003-025-07587-x. Commun Biol. 2025. PMID: 39920323 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Menjot de Champfleur N, Lima Maldonado I, Moritz-Gasser Set al. Middle longitudinal fasciculus delineation within language pathways: a diffusion tensor imaging study in human. Eur J Radiol. 2013;82(1):151-157. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

