No Increase in Survival for 36-mm versus 32-mm Femoral Heads in Metal-on-polyethylene THA: A Registry Study
- PMID: 30260863
- PMCID: PMC6259897
- DOI: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000000508
No Increase in Survival for 36-mm versus 32-mm Femoral Heads in Metal-on-polyethylene THA: A Registry Study
Abstract
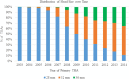
Background: During the past decade, the 32-mm head has replaced the 28-mm head as the most common head size used in primary THA in many national registries, and the use of 36-mm heads has also increased. However, it is unclear whether 32-mm and 36-mm heads decrease the revision risk in metal-on-polyethylene (MoP) THA compared with 28-mm heads.
Questions/purposes: (1) In the setting of the Nordic Arthroplasty Register Association database, does the revision risk for any reason differ among 28-, 32-, and 36-mm head sizes in patients undergoing surgery with MoP THA? (2) Does the revision risk resulting from dislocation decrease with increasing head diameter (28-36 mm) in patients undergoing surgery with MoP THA in the same registry?
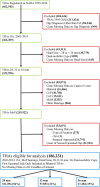
Methods: Data were derived from the Nordic Arthroplasty Register Association database, a collaboration among the national arthroplasty registries of Denmark, Finland, Norway, and Sweden. Patients with primary osteoarthritis who had undergone primary THA with a 28-, 32-, or 36-mm MoP bearing from 2003 to 2014 were included. Patients operated on with dual-mobility cups were excluded. In patients with bilateral THA, only the first operated hip was included. After applying the inclusion criteria, the number of patients and THAs with a complete data set was determined to be 186,231, which accounted for 51% of all hips (366,309) with primary osteoarthritis operated on with THA of any head size and bearing type during the study observation time. Of the included patients, 60% (111,046 of 186,231) were women, the mean age at surgery was 70 (± 10) years, and the median followup was 4.5 years (range, 0-14 years). A total of 101,094 patients had received a 28-mm, 57,853 a 32-mm, and 27,284 a 36-mm head with 32 mm used as the reference group. The revision of any component for any reason was the primary outcome and revision for dislocation was the secondary outcome. Very few patients are estimated to be lost to followup because emigration in the population of interest (older than 65-70 years) is rare. A Kaplan-Meier analysis was used to estimate THA survival for each group, whereas Cox regression models were fitted to calculate hazard ratios (HRs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for THA revision comparing the 28- and 36-mm head diameters with the 32-mm head diameters adjusting for age, sex, year of surgery, type of cup and stem fixation, polyethylene type (crosslinked versus conventional), and surgical approach.
Results: In the adjusted Cox regression model, there was no difference in the adjusted risk for revision for any reason between patients with 28-mm (HR, 1.06; 95% CI, 0.97-0.16) and 32-mm heads, whereas the risk of revision was higher for patients with 36-mm heads (HR, 1.14; 95% CI, 1.04-1.26) compared with patients with 32-mm heads. Patients with 28-mm heads had a higher risk of revision for dislocation (HR, 1.67; 95% CI, 1.38-1.98) compared with 32 mm, whereas there was no difference between patients with 36-mm (HR, 0.85; 95% CI, 0.70-1.02) and 32-mm heads.
Conclusions: After adjusting for relevant confounding variables, we found no benefits for 32-mm heads against 28 mm in terms of overall revision risk. However, when dislocation risk is considered, 32-mm heads would be a better option, because they had a lower risk of revision resulting from dislocation. There were no benefits with the use of 36-mm heads over 32 mm, because the transition from 32 to 36 mm was associated with a higher risk of revision for all reasons, which was not accompanied by a decrease in the risk of revision resulting from dislocation. The use of 32-mm heads appears to offer the best compromise between joint stability and other reasons for revision in MoP THA. Further studies with longer followup, especially of 36-mm heads, as well as better balance of confounders across head sizes and better control of patient-related risk factors for THA revision are needed.
Level of evidence: Level III, therapeutic study.
Conflict of interest statement
All ICMJE Conflict of Interest Forms for authors and
Figures
Comment in
-
CORR Insights®: No Increase in Survival for 36-mm versus 32-mm Femoral Heads in Metal-on-polyethylene THA: A Registry Study.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2018 Dec;476(12):2379-2380. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000000546. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2018. PMID: 30379681 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- AOANJRR Australian Orthopaedic Association National Joint Replacement Registry. Annual report 2017: hip, knee & shoulder arthroplasty. Available at: https://aoanjrr.sahmri.com/documents/10180/397736/Hip%2C%20Knee%20%26%20.... Accessed October 11, 2017.
-
- Berry DJ, von Knoch M, Schleck CD, Harmsen WS. Effect of femoral head diameter and operative approach on risk of dislocation after primary total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87:2456–2463. - PubMed
-
- Burroughs BR, Hallstrom B, Golladay GJ, Hoeffel D, Harris WH. Range of motion and stability in total hip arthroplasty with 28-, 32-, 38-, and 44-mm femoral head sizes. J Arthroplasty. 2005;20:11–19. - PubMed
-
- Bystrom S, Espehaug B, Furnes O, Havelin LI; Norwegian Arthroplasty Register. Femoral head size is a risk factor for total hip luxation: a study of 42,987 primary hip arthroplasties from the Norwegian Arthroplasty Register. Acta Orthop Scand. 2003;74:514–524. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

