Inspiratory muscle weakness contributes to exertional dyspnea in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension
- PMID: 30260970
- PMCID: PMC6160017
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0204072
Inspiratory muscle weakness contributes to exertional dyspnea in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension
Abstract
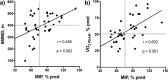
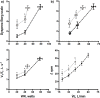
Determination of potentially-reversible factors contributing to exertional dyspnea remains an unmet clinical need in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH). Therefore, we aimed to evaluate the influence of inspiratory muscle weakness (IMW) on exercise capacity and dyspnea during effort in patients with CTEPH. We performed a prospective cross-sectional study that included thirty-nine consecutive patients with CTEPH (48 ± 15 yrs, 61% female) confirmed by right heart catheterization that underwent an incremental cardiopulmonary exercise test, 6-minute walk test and maximum inspiratory pressure (MIP) measurement. MIP < 70%pred was found in 46% of patients. On a multiple linear regression analysis, MIP was independently associated with 6MWD and [Formula: see text]. Patients with MIP < 70% presented greater [Formula: see text] than those with MIP ≥ 70%. Additionally, they also presented stronger sensations of dyspnea throughout exercise, even when adjusted for ventilation. At rest and at different levels of exercise, mean inspiratory flow (VT/TI) was significantly higher in patients with MIP < 70%. In conclusion, IMW is associated with a rapid increase of dyspnea, higher inspiratory load and poor exercise capacity in patients with CTEPH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Madani MM, Auger WR, Pretorius V, Sakakibara N, Kerr KM, Kim NH, et al. Pulmonary endarterectomy: recent changes in a single institution's experience of more than 2,700 patients. The Annals of thoracic surgery. 2012;94(1):97–103; discussion Epub 2012/05/26. 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2012.04.004 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mayer E, Jenkins D, Lindner J, D'Armini A, Kloek J, Meyns B, et al. Surgical management and outcome of patients with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: results from an international prospective registry. The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery. 2011;141(3):702–10. Epub 2011/02/22. 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2010.11.024 . - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

