Cilostazol disrupts TLR-4, Akt/GSK-3β/CREB, and IL-6/JAK-2/STAT-3/SOCS-3 crosstalk in a rat model of Huntington's disease
- PMID: 30260985
- PMCID: PMC6160003
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0203837
Cilostazol disrupts TLR-4, Akt/GSK-3β/CREB, and IL-6/JAK-2/STAT-3/SOCS-3 crosstalk in a rat model of Huntington's disease
Abstract
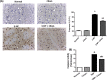
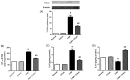
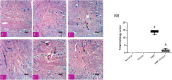
Countless neurodegenerative diseases are associated with perverse multiple targets of cyclic nucleotide signalling, hastening neuronal death. Cilostazol, a phosphodiesterase-III inhibitor, exerts neuroprotective effects against sundry models of neurotoxicity, however, its role against Huntington's disease (HD) has not yet been tackled. Hence, its modulatory effect on several signalling pathways using the 3-nitropropionic acid (3-NP) model was conducted. Animals were injected with 3-NP (10 mg/kg/day, i.p) for two successive weeks with or without the administration of cilostazol (100 mg/kg/day, p.o.). Contrary to the 3-NP effects, cilostazol largely preserved striatal dopaminergic neurons, improved motor coordination, and enhanced the immunohistochemical reaction of tyrosine hydroxylase enzyme. The anti-inflammatory effect of cilostazol was documented by the pronounced reduction of the toll like receptor-4 (TLR-4) protein expression and the inflammatory cytokine IL-6, but with a marked elevation in IL-10 striatal contents. As a consequence, cilostazol reduced IL-6 downstream signal, where it promoted the level of suppressor of cytokine signalling 3 (SOCS3), while abated the phosphorylation of Janus Kinase 2 (JAK-2) and Signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 (STAT-3). Phosphorylation of the protein kinase B/glycogen synthase kinase-3β/cAMP response element binding protein (Akt/GSK-3β/CREB) cue is another signalling pathway that was modulated by cilostazol to further signify its anti-inflammatory and antiapoptotic capacities. The latter was associated with a reduction in the caspase-3 expression assessed by immunohistochemical assay. In conclusion the present study provided a new insight into the possible mechanisms by which cilostazol possesses neuroprotective properties. These intersecting mechanisms involve the interference between TLR-4, IL-6-IL-10/JAK-2/STAT-3/SOCS-3, and Akt/GSK-3β/CREB signalling pathways.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




References
-
- Leegwater-Kim J, Cha J-HJ. The Paradigm of Huntington’s Disease: Therapeutic Opportunities in Neurodegeneration. NeuroRx. 2004; 1: 128–138. Available: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC534918/%5Cnhttp://www.ncbi.n... 10.1602/neurorx.1.1.128 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alexi T, Hughes PE, Faull RL, Williams CE. 3-Nitropropionic acid’s lethal triplet: cooperative pathways of neurodegeneration. Neuroreport. 1998; 9: R57–R64. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

