Measurements, Thermodynamic Modeling, and a Hydrogen Bonding Study on the Solubilities of Metoprolol Succinate in Organic Solvents
- PMID: 30261636
- PMCID: PMC6222524
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules23102469
Measurements, Thermodynamic Modeling, and a Hydrogen Bonding Study on the Solubilities of Metoprolol Succinate in Organic Solvents
Abstract
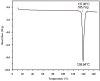
The solubilities of metoprolol succinate (a cardioselective β1 adrenergic receptor) in methanol, ethanol, n-propanol, isopropanol, n-butanol, ethyl acetate, and acetone were measured at temperatures ranging from (278.2 to 318.2) K using a solid⁻liquid equilibrium method. The solubility of metoprolol succinate increases with increasing temperature. At a fixed temperature, the solubility decreases in the order methanol > ethanol > n-butanol > n-propanol > isopropanol > acetone > ethyl acetate. The enthalpy of fusion and the melting point of metoprolol succinate were determined by differential scanning calorimetry. The thermodynamic properties of the dissolution process, determined by a van't Hoff analysis, have been obtained and are discussed. The modified Apelblat equation, Wilson model, and non-random two-liquid (NRTL) model were employed to correlate the solubilities of metoprolol succinate in different solvents. Finally, a quantitative structure⁻property relationship (QSPR) study of physical properties of solvents and density functional theory simulations of hydrogen-bonding structure were carried out to give the explanation for the sequence of solubility in alcohols. The density functional theory (DFT) calculations well illustrated that the solubility of metoprolol succinate in various alcohols can be mainly attributed to the intra- and intermolecular hydrogen bonds in metoprolol succinate-solvent complexes.
Keywords: dissolution enthalpy; hydrogen bonding; metoprolol succinate; solubility; thermodynamic model.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Solubility measurement, Hansen solubility parameters and solution thermodynamics of gemfibrozil in different pharmaceutically used solvents.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2019 Aug;45(8):1258-1264. doi: 10.1080/03639045.2019.1594884. Epub 2019 May 14. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2019. PMID: 30995878
-
Measurement and Correlation of Solubility of Thiamine Nitrate in Three Binary Solvents and Thermodynamic Properties for the Solutions in Different Binary Mixtures at (278.15-313.15) K.Molecules. 2023 Jun 27;28(13):5012. doi: 10.3390/molecules28135012. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37446674 Free PMC article.
-
Phase equilibria and thermodynamics of p-hydroxybenzoic acid.J Pharm Sci. 2006 Apr;95(4):748-60. doi: 10.1002/jps.20569. J Pharm Sci. 2006. PMID: 16447178
-
Solubility of Omeprazole Sulfide in Different Solvents at the Range of 280.35-319.65 K.J Solution Chem. 2013;42(12):2342-2353. doi: 10.1007/s10953-013-0110-y. Epub 2013 Nov 12. J Solution Chem. 2013. PMID: 24319302 Free PMC article.
-
Noncovalent organocatalysis based on hydrogen bonding: elucidation of reaction paths by computational methods.Top Curr Chem. 2010;291:1-27. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-02815-1_3. Top Curr Chem. 2010. PMID: 21494946 Review.
Cited by
-
Independent Tailoring of Dose and Drug Release via a Modularized Product Design Concept for Mass Customization.Pharmaceutics. 2020 Aug 14;12(8):771. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12080771. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 32823877 Free PMC article.
-
Solubility and Thermodynamic Data of Febuxostat in Various Mono Solvents at Different Temperatures.Molecules. 2022 Jun 23;27(13):4043. doi: 10.3390/molecules27134043. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35807294 Free PMC article.
-
Introduction to "Intramolecular Hydrogen Bonding 2018".Molecules. 2019 Aug 7;24(16):2858. doi: 10.3390/molecules24162858. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31394716 Free PMC article.
-
Solubilization and Thermodynamic Analysis of Isotretinoin in Eleven Different Green Solvents at Different Temperatures.Materials (Basel). 2022 Nov 21;15(22):8274. doi: 10.3390/ma15228274. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36431759 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Frishman W.H., Hainer J.W., Sugg J. A factorial study of combination hypertension treatment with metoprolol succinate extended release and felodipine extended, release: Results of the metoprolol succinate-felodipine antihypertension combination trial (M-FACT) Am. J. Hypertens. 2006;19:388–395. doi: 10.1016/j.amjhyper.2005.10.007. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen H.S., Chen Y., Yuan L. Synthesis of related substances E and J of metoprolol. Chin. J. Med. Chem. 2013;23:393–396.
-
- Chen J., Sarma B., Evans J.M.B., Myerson A.S. Pharmaceutical crystallization. Cryst. Growth Des. 2011;11:887–895. doi: 10.1021/cg101556s. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

