A review of recent publication trends from top publishing countries
- PMID: 30261915
- PMCID: PMC6161455
- DOI: 10.1186/s13643-018-0819-1
A review of recent publication trends from top publishing countries
Abstract
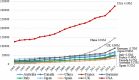
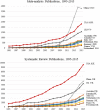
Background: Evidence-based medicine relies on current best evidence from the medical literature, the patient's history, and the clinician's own experience to provide the best care for patients. Systematic reviews and meta-analysis are considered the highest levels of evidence for informing clinical decisions. Recently, reports have shown an increase in the number but a decrease in quality of meta-analysis publications. We reviewed publication trends and determined the countries with the most journal articles and types of publications in PubMed from 1995 to 2015.
Methods: We examined journal entries in PubMed from 1995 to 2015 from top publishing countries for total number of publications and citations in core clinical journals and in specific publication types (systematic reviews, meta-analysis, randomized controlled trials).
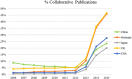
Results: Yearly, only 30 countries generated 94.6% of all publications and 98.1% of core clinical journals worldwide. All publication types increased but with a significant increase in meta-analysis publications from China. Collaborative and co-authored papers among the 30 countries also showed an increasing trend.
Conclusion: The USA leads in all publication citations and specific publication types, except for meta-analysis where China publishes more. Collaborative publishing among international collaborators is also increasing.
Keywords: Collaborative publishing; Evidence-based medicine; Meta-analysis; PubMed; Publication type; Systematic review.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

