Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) as a Cancer Biomarker and MMP-9 Biosensors: Recent Advances
- PMID: 30262739
- PMCID: PMC6211011
- DOI: 10.3390/s18103249
Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) as a Cancer Biomarker and MMP-9 Biosensors: Recent Advances
Abstract
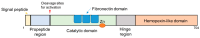
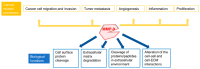
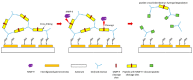
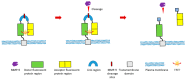
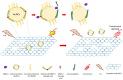
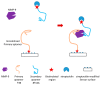
As one of the most widely investigated matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), MMP-9 is a significant protease which plays vital roles in many biological processes. MMP-9 can cleave many extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins to regulate ECM remodeling. It can also cleave many plasma surface proteins to release them from the cell surface. MMP-9 has been widely found to relate to the pathology of cancers, including but not limited to invasion, metastasis and angiogenesis. Some recent research evaluated the value of MMP-9 as biomarkers to various specific cancers. Besides, recent research of MMP-9 biosensors discovered various novel MMP-9 biosensors to detect this enzyme. In this review, some recent advances in exploring MMP-9 as a biomarker in different cancers are summarized, and recent discoveries of novel MMP-9 biosensors are also presented.
Keywords: biomarker; biosensor; cancer detection; cancers; matrix metalloproteinase-9; matrix metalloproteinases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

