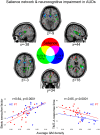
Salience network structural integrity predicts executive impairment in alcohol use disorders
- PMID: 30262893
- PMCID: PMC6160480
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-32828-x
Salience network structural integrity predicts executive impairment in alcohol use disorders
Abstract
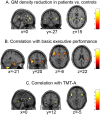
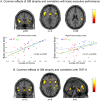
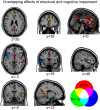
The neural bases of cognitive impairment(s) in alcohol use disorders (AUDs) might reflect either a global brain damage underlying different neuro-cognitive alterations, or the involvement of specific regions mostly affected by alcohol neuro-toxic effects. While voxel-based-morphometry (VBM) studies have shown a distributed atrophic pattern in fronto-limbic and cerebellar structures, the lack of comprehensive neuro-cognitive assessments prevents previous studies from drawing robust inferences on the specificity of the association between neuro-structural and cognitive impairments in AUDs. To fill this gap, we addressed the neuro-structural bases of cognitive impairment in AUDs, by coupling VBM with an in-depth neuropsychological assessment. VBM results highlighted a diffuse pattern of grey matter reduction in patients, involving the key-nodes of the meso-cortico-limbic (striatum, hippocampus, medial prefrontal cortex), salience (insular and dorsal anterior cingulate cortex) and executive (inferior frontal cortex) networks. Grey matter density in the insular and anterior cingulate sectors of the salience network, significantly decreased in patients, explained almost half of variability in their defective attentional and working-memory performance. The multiple cognitive and neurological impairments observed in AUDs might thus reflect a specific executive deficit associated with the selective damage of a salience-based neural mechanism enhancing access to cognitive resources required for controlled cognition and behaviour.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Abnormal fronto-striatal intrinsic connectivity reflects executive dysfunction in alcohol use disorders.Cortex. 2019 Jun;115:27-42. doi: 10.1016/j.cortex.2019.01.004. Epub 2019 Jan 23. Cortex. 2019. PMID: 30738999
-
Relations between cognitive and motor deficits and regional brain volumes in individuals with alcoholism.Brain Struct Funct. 2019 Jul;224(6):2087-2101. doi: 10.1007/s00429-019-01894-w. Epub 2019 Jun 3. Brain Struct Funct. 2019. PMID: 31161472 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations in Cognition-Related Cerebello-Cerebral Networks in Multiple System Atrophy.Cerebellum. 2019 Aug;18(4):770-780. doi: 10.1007/s12311-019-01031-7. Cerebellum. 2019. PMID: 31069705
-
[Structural and functional neuroanatomy of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)].Encephale. 2009 Apr;35(2):107-14. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2008.01.005. Epub 2008 Jul 7. Encephale. 2009. PMID: 19393378 Review. French.
-
Gray Matter Atrophy within the Default Mode Network of Fibromyalgia: A Meta-Analysis of Voxel-Based Morphometry Studies.Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:7296125. doi: 10.1155/2016/7296125. Epub 2016 Dec 26. Biomed Res Int. 2016. PMID: 28105430 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Meta-analysis of grey matter changes and their behavioral characterization in patients with alcohol use disorder.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 4;11(1):5238. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-84804-7. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33664372 Free PMC article.
-
Microstructural damage of white-matter tracts connecting large-scale networks is related to impaired executive profile in alcohol use disorder.Neuroimage Clin. 2020;25:102141. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2019.102141. Epub 2019 Dec 23. Neuroimage Clin. 2020. PMID: 31927501 Free PMC article.
-
Common Gray Matter Reductions in Alcohol Use and Obsessive-Compulsive Disorders: A Meta-analysis.Biol Psychiatry Glob Open Sci. 2021 Nov 27;2(4):421-431. doi: 10.1016/j.bpsgos.2021.11.010. eCollection 2022 Oct. Biol Psychiatry Glob Open Sci. 2021. PMID: 36324652 Free PMC article.
-
Let's focus on the insula in addiction: A refined anatomical exploration of insula in severe alcohol and cocaine use disorders.Eur Psychiatry. 2024 Nov 15;67(1):e75. doi: 10.1192/j.eurpsy.2024.1784. Eur Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39543913 Free PMC article.
-
Resting State Functional Connectivity Patterns Associate with Alcohol Use Disorder Characteristics: Insights from the Triple Network Model.ArXiv [Preprint]. 2025 Apr 8:arXiv:2504.06199v1. ArXiv. 2025. PMID: 40297229 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
-
- WHO. Global status report on alcohol and health. World Heal. Organ. 1–100 (2014).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

