A single reporter mouse line for Vika, Flp, Dre, and Cre-recombination
- PMID: 30262904
- PMCID: PMC6160450
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-32802-7
A single reporter mouse line for Vika, Flp, Dre, and Cre-recombination
Abstract
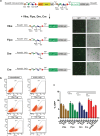
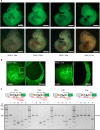
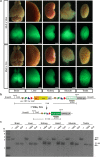
Site-specific recombinases (SSR) are utilized as important genome engineering tools to precisely modify the genome of mice and other model organisms. Reporter mice that mark cells that at any given time had expressed the enzyme are frequently used for lineage tracing and to characterize newly generated mice expressing a recombinase from a chosen promoter. With increasing sophistication of genome alteration strategies, the demand for novel SSR systems that efficiently and specifically recombine their targets is rising and several SSR-systems are now used in combination to address complex biological questions in vivo. Generation of reporter mice for each one of these recombinases is cumbersome and increases the number of mouse lines that need to be maintained in animal facilities. Here we present a multi-reporter mouse line for loci-of-recombination (X) (MuX) that streamlines the characterization of mice expressing prominent recombinases. MuX mice constitutively express nuclear green fluorescent protein after recombination by either Cre, Flp, Dre or Vika recombinase, rationalizing the number of animal lines that need to be maintained. We also pioneer the use of the Vika/vox system in mice, illustrating its high efficacy and specificity, thereby facilitating future designs of sophisticated recombinase-based in vivo genome engineering strategies.
Conflict of interest statement
The Vika/vox System is patent protected (EP 26 90 177 B1). The authors FB and MK declare financial competing interests. The other authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dre recombinase, like Cre, is a highly efficient site-specific recombinase in E. coli, mammalian cells and mice.Dis Model Mech. 2009 Sep-Oct;2(9-10):508-15. doi: 10.1242/dmm.003087. Epub 2009 Aug 19. Dis Model Mech. 2009. PMID: 19692579
-
Vika/vox, a novel efficient and specific Cre/loxP-like site-specific recombination system.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Jan;41(2):e37. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks1037. Epub 2012 Nov 9. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23143104 Free PMC article.
-
Novel reporter and deleter mouse strains generated using VCre/VloxP and SCre/SloxP systems, and their system specificity in mice.Transgenic Res. 2018 Apr;27(2):193-201. doi: 10.1007/s11248-018-0067-0. Epub 2018 Mar 15. Transgenic Res. 2018. PMID: 29546522
-
Mammalian genome targeting using site-specific recombinases.Front Biosci. 2006 Jan 1;11:1108-36. doi: 10.2741/1867. Front Biosci. 2006. PMID: 16146801 Review.
-
Site-specific recombinases for manipulation of the mouse genome.Methods Mol Biol. 2009;561:245-63. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60327-019-9_16. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19504076 Review.
Cited by
-
Principles of Genetic Engineering.Genes (Basel). 2020 Mar 10;11(3):291. doi: 10.3390/genes11030291. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32164255 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thy1 promoter activity in the Rosa26 locus in mice: lessons from Dre-rox conditional expression system.Exp Anim. 2020 Aug 5;69(3):287-294. doi: 10.1538/expanim.20-0002. Epub 2020 Feb 11. Exp Anim. 2020. PMID: 32051391 Free PMC article.
-
Neurobiology of cannabinoid receptor signaling .Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2020 Sep;22(3):207-222. doi: 10.31887/DCNS.2020.22.3/blutz. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33162764 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A most formidable arsenal: genetic technologies for building a better mouse.Genes Dev. 2020 Oct 1;34(19-20):1256-1286. doi: 10.1101/gad.342089.120. Genes Dev. 2020. PMID: 33004485 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential CRH expression level determines efficiency of Cre- and Flp-dependent recombination.Front Neurosci. 2023 Aug 3;17:1163462. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1163462. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37599997 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

