The PI3K/AKT pathway in obesity and type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 30263000
- PMCID: PMC6158718
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.27173
The PI3K/AKT pathway in obesity and type 2 diabetes
Abstract
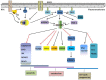
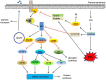
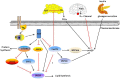
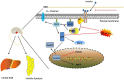
Obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus are complicated metabolic diseases that affect multiple organs and are characterized by hyperglycaemia. Currently, stable and effective treatments for obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus are not available. Therefore, the mechanisms leading to obesity and diabetes and more effective ways to treat obesity and diabetes should be identified. Based on accumulated evidences, the PI3K/AKT signalling pathway is required for normal metabolism due to its characteristics, and its imbalance leads to the development of obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus. This review focuses on the role of PI3K/AKT signalling in the skeletal muscle, adipose tissue, liver, brain and pancreas, and discusses how this signalling pathway affects the development of the aforementioned diseases. We also summarize evidences for recently identified therapeutic targets of the PI3K/AKT pathway as treatments for obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus. PI3K/AKT pathway damaged in various tissues of the body leads to obesity and type 2 diabetes as the result of insulin resistance, and in turn, insulin resistance exacerbates the PI3K/AKT pathway, forming a vicious circle.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PHLPP: a putative cellular target during insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.J Endocrinol. 2017 Jun;233(3):R185-R198. doi: 10.1530/JOE-17-0081. Epub 2017 Apr 20. J Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 28428363 Review.
-
Gallic acid attenuates high-fat diet fed-streptozotocin-induced insulin resistance via partial agonism of PPARγ in experimental type 2 diabetic rats and enhances glucose uptake through translocation and activation of GLUT4 in PI3K/p-Akt signaling pathway.Eur J Pharmacol. 2014 Dec 15;745:201-16. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.10.044. Epub 2014 Nov 5. Eur J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25445038
-
Insulin sensitization via partial agonism of PPARγ and glucose uptake through translocation and activation of GLUT4 in PI3K/p-Akt signaling pathway by embelin in type 2 diabetic rats.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Jan;1830(1):2243-55. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2012.10.016. Epub 2012 Oct 24. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23104384
-
The PI3K/Akt signaling axis and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM): From mechanistic insights into possible therapeutic targets.Cell Biol Int. 2024 Aug;48(8):1049-1068. doi: 10.1002/cbin.12189. Epub 2024 May 29. Cell Biol Int. 2024. PMID: 38812089 Review.
-
Irisin inhibits hepatic gluconeogenesis and increases glycogen synthesis via the PI3K/Akt pathway in type 2 diabetic mice and hepatocytes.Clin Sci (Lond). 2015 Nov;129(10):839-50. doi: 10.1042/CS20150009. Epub 2015 Jul 13. Clin Sci (Lond). 2015. PMID: 26201094
Cited by
-
Cassia Abbreviata Enhances Glucose Uptake and Glucose Transporter 4 Translocation in C2C12 Mouse Skeletal Muscle Cells.J Evid Based Integr Med. 2021 Jan-Dec;26:2515690X211006333. doi: 10.1177/2515690X211006333. J Evid Based Integr Med. 2021. PMID: 33788626 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of metabolites associated with prostate cancer risk: a nested case-control study with long follow-up in the Northern Sweden Health and Disease Study.BMC Med. 2020 Jul 23;18(1):187. doi: 10.1186/s12916-020-01655-1. BMC Med. 2020. PMID: 32698845 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Hydrolyzed Bird's Nest on β-Cell Function and Insulin Signaling in Type 2 Diabetic Mice.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Apr 13;12:632169. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.632169. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33986669 Free PMC article.
-
Cistanche tubulosa phenylethanoid glycosides suppressed adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and improved obesity and insulin resistance in high-fat diet induced obese mice.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022 Oct 13;22(1):270. doi: 10.1186/s12906-022-03743-6. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022. PMID: 36229811 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the Variants Located in the MIR196A2, MIR146A, and MIR423 with Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus in Pakistani Population.Genes (Basel). 2021 Apr 28;12(5):664. doi: 10.3390/genes12050664. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33925232 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barnett R. Obesity. The Lancet. 2017;389(10069):591.
-
- Wang YC, McPherson K, Marsh T, Gortmaker SL, Brown M. Health and economic burden of the projected obesity trends in the USA and the UK. Lancet. 2011;378(9793):815–25. - PubMed
-
- Holman RR. Type 2 diabetes mellitus in 2012: Optimal management of T2DM remains elusive. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2013;9(2):67–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

