Triptolide Attenuates Renal Tubular Epithelial-mesenchymal Transition Via the MiR-188-5p-mediated PI3K/AKT Pathway in Diabetic Kidney Disease
- PMID: 30263007
- PMCID: PMC6158722
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.24032
Triptolide Attenuates Renal Tubular Epithelial-mesenchymal Transition Via the MiR-188-5p-mediated PI3K/AKT Pathway in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Abstract
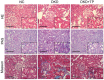
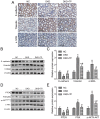
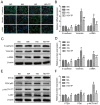
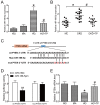
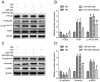
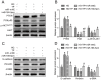
Triptolide possesses the trait of renal protection. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is closely linked to the pathogenesis of diabetic kidney disease (DKD). MicroRNAs have recently emerged as critical regulators of DKD. However, it is poorly understood whether triptolide alleviates renal EMT by regulating microRNAs in DKD. In this study, we found that triptolide decreased albuminuria, improved the renal structure and reduced renal EMT in rats with DKD. Furthermore, activation of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway was increased in diabetic rats, which was partly reversed by triptolide. Triptolide also alleviated glucose-induced EMT in HK-2 cells in vitro. PI3K/AKT signaling pathway activation was reduced after triptolide treatment. Moreover, triptolide decreased the increase in miR-188-5p expression stimulated by high glucose levels in HK-2 cells. miR-188-5p inhibited PTEN expression by directly interacting with the PTEN 3'-untranslated region. Additionally, downregulation of miR-188-5p, which imitates the effects of triptolide, attenuated the activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway and HG-induced EMT, whereas miR-188-5p overexpression reversed the effects of triptolide on the PI3K/AKT pathway and EMT. In conclusion, we demonstrated that triptolide ameliorates renal EMT via the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway through the interaction between miR-188-5p and PTEN, indicating that miR-188-5p may be a therapeutic target of triptolide in DKD.
Keywords: Diabetic kidney disease.; Epithelial-mesenchymal transition; MiR-188-5p; PTEN; Triptolide.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
miR-29b regulates Ang II-induced EMT of rat renal tubular epithelial cells via targeting PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.Int J Mol Med. 2018 Jul;42(1):453-460. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3579. Epub 2018 Mar 22. Int J Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29568897
-
Triptolide prevents extracellular matrix accumulation in experimental diabetic kidney disease by targeting microRNA-137/Notch1 pathway.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Mar;233(3):2225-2237. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26092. Epub 2017 Sep 13. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 28695984
-
Effects and mechanism of miR-23b on glucose-mediated epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in diabetic nephropathy.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2016 Jan;70:149-60. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2015.11.016. Epub 2015 Dec 2. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 26646104
-
Perspectives on the role of PTEN in diabetic nephropathy: an update.Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2020 Nov;57(7):470-483. doi: 10.1080/10408363.2020.1746735. Epub 2020 Apr 20. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2020. PMID: 32306805 Review.
-
Effect of miR-21 on Renal Fibrosis Induced by Nano-SiO₂ in Diabetic Nephropathy Rats via PTEN/AKT Pathway.J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2021 Feb 1;21(2):1079-1084. doi: 10.1166/jnn.2021.18631. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33183446 Review.
Cited by
-
Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Analysis Exploring the Mechanism of Tripterygium wilfordii in the Treatment of Oral Lichen Planus.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Aug 10;59(8):1448. doi: 10.3390/medicina59081448. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 37629739 Free PMC article.
-
Jiawei Shengjiangsan's Effect on Renal Injury in Diabetic Nephropathy Mice is Investigated via the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB Signaling Pathway.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024 Apr 12;17:1687-1698. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S456205. eCollection 2024. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024. PMID: 38629025 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of MicroRNA in Contrast-Induced Nephropathy: A Scoping Review and Meta-Analysis.Biomed Res Int. 2020 May 21;2020:4189621. doi: 10.1155/2020/4189621. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32596306 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA HOX transcript antisense RNA mediates hyperglycemic-induced injury in the renal tubular epithelial cell via the miR-126-5pAkt axis.Aging Med (Milton). 2023 Sep 27;6(4):427-434. doi: 10.1002/agm2.12266. eCollection 2023 Dec. Aging Med (Milton). 2023. PMID: 38239710 Free PMC article.
-
Based on Network Pharmacology Tools to Investigate the Mechanism of Tripterygium wilfordii Against IgA Nephropathy.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Dec 15;8:794962. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.794962. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34977095 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Himmelfarb J, Tuttle KR. New therapies for diabetic kidney disease. The New England journal of medicine. 2013;369:2549–50. - PubMed
-
- Guo K, Zhang L, Zhao F, Lu J, Pan P, Yu H. et al. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease and associated factors in Chinese individuals with type 2 diabetes: Cross-sectional study. Journal of diabetes and its complications. 2016;30:803–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

