t-BHQ Protects Against Oxidative Damage and Maintains the Antioxidant Response in Malnourished Rats
- PMID: 30263018
- PMCID: PMC6156215
- DOI: 10.1177/1559325818796304
t-BHQ Protects Against Oxidative Damage and Maintains the Antioxidant Response in Malnourished Rats
Abstract
Objective: Tert-butylhydroquinone (t-BHQ) protective effect against oxidative damage in thymus from malnourished pops-rats was evaluated.
Methods: Malnutrition in pops-rats was induced during the lactation period and first-, second-, and third-degree malnourished rats were studied (MN1, MN2, and MN3). To determine t-BHQ protective effect, lipid peroxidation (LPx) was assessed, as well as the carbonyl content. The reduced glutathione and glutathione disulfide content were determined and antioxidant enzyme activities were measured.
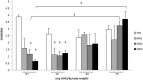
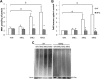
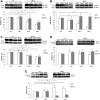
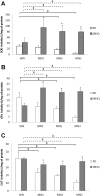
Results: Oxidative protein damage, LPx, and Nuclear Factor-κB (NF-κB) content, increased in the MN2 and MN3 compared to well-nourished rats, associated with lower protein content and antioxidant activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), and catalase. Tert-butylhydroquinone treatment induced a protective effect against lipids and proteins oxidative damage, as well as decrease in NF-κB in MN rats and restored the antioxidant mechanisms, mostly GPx and SOD. No differences were found between male and female animals.
Conclusions: Results show that higher body weight deficit leads to increased oxidative damage and probably inflammation, attributable to alterations in antioxidant mechanisms. These effects were reversed by the t-BHQ-treatment, which restores the antioxidant response. Our findings suggest that t-BHQ could be an interesting pharmacological intervention, but it needs to be studied further.
Keywords: NF-κB; antioxidants; malnutrition; oxidative stress; t-BHQ.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests: The author(s) declared the following potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. Rosas-Trejo and Toledo-Pérez are CONACYT scholarship holders.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oxidative damage and antioxidant defense in thymus of malnourished lactating rats.Nutrition. 2015 Nov-Dec;31(11-12):1408-15. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2015.05.014. Epub 2015 Jun 6. Nutrition. 2015. PMID: 26429663
-
Effects of oxidative stress caused by tert-butylhydroquinone on cytotoxicity in MDCK cells.J Vet Med Sci. 2012 May;74(5):583-9. doi: 10.1292/jvms.11-0412. Epub 2011 Dec 19. J Vet Med Sci. 2012. PMID: 22185773
-
The involvement of Nrf2 in the protective effects of diallyl disulfide on carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic oxidative damage and inflammatory response in rats.Food Chem Toxicol. 2014 Jan;63:174-85. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2013.11.006. Epub 2013 Nov 15. Food Chem Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 24246655
-
Glutamate ameliorates copper-induced oxidative injury by regulating antioxidant defences in fish intestine.Br J Nutr. 2016 Jul;116(1):70-9. doi: 10.1017/S0007114516001732. Epub 2016 May 17. Br J Nutr. 2016. PMID: 27184647
-
Quercetin modulates OTA-induced oxidative stress and redox signalling in HepG2 cells - up regulation of Nrf2 expression and down regulation of NF-κB and COX-2.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Jan;1840(1):681-92. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.10.024. Epub 2013 Oct 24. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24161694
Cited by
-
Comparison of Superoxide Dismutase Activity at the Cell, Organ, and Whole-Body Levels.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025 Apr 7. doi: 10.1007/s12013-025-01708-3. Online ahead of print. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025. PMID: 40192904 Review.
-
Promoting Nrf2/Sirt3-Dependent Mitophagy Suppresses Apoptosis in Nucleus Pulposus Cells and Protects against Intervertebral Disc Degeneration.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Jun 9;2021:6694964. doi: 10.1155/2021/6694964. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 34211633 Free PMC article.
-
TBHQ-Overview of Multiple Mechanisms against Oxidative Stress for Attenuating Methamphetamine-Induced Neurotoxicity.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Nov 27;2020:8874304. doi: 10.1155/2020/8874304. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 33354283 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metformin and tBHQ Treatment Combined with an Exercise Regime Prevents Osteosarcopenic Obesity in Middle-Aged Wistar Female Rats.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Aug 14;2021:5294266. doi: 10.1155/2021/5294266. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 34447486 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mehta NM, Corkins MR, Lyman B, et al. ; American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition Board of Directors. Defining pediatric malnutrition: a paradigm shift toward etiology-related definitions. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2013;37(4):460–481. - PubMed
-
- United Nations Children’s Fund, World Health Organization, World Bank Group. Joint Child Malnutrition Estimates—Levels and Trends. New York, NY: UNICEF; Geneva, GE, Switzerland: WHO; Washington, WA: WBG; 2016.
-
- Katona P, Katona-Apte J. The interaction between nutrition and infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;46(10):1582–1588. - PubMed
-
- Savino W, Dardenne M, Velloso LA, Dayse Silva-Barbosa S. The thymus is a common target in malnutrition and infection. Br J Nutr. 2007;98(S1):S11–S16. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

