Bamboo (Phyllostachys bambusoides) leaf extracts inhibit adipogenesis by regulating adipogenic transcription factors and enzymes in 3T3-L1 adipocytes
- PMID: 30263634
- PMCID: PMC6049548
- DOI: 10.1007/s10068-017-0150-y
Bamboo (Phyllostachys bambusoides) leaf extracts inhibit adipogenesis by regulating adipogenic transcription factors and enzymes in 3T3-L1 adipocytes
Abstract
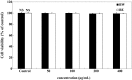
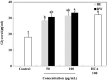
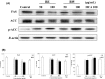
In this study, the inhibitory effects of bamboo leaf extracts on adipogenesis were investigated by evaluating their activity against adipogenic transcription factors and enzymes in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Bamboo leaf extracts significantly decreased triglyceride levels, and increased glycerol release in adipocytes. Cells treated with the water extract showed significantly higher glycerol release as well as lower triglyceride contents than those treated with the ethanol extract. Both bamboo leaf extracts significantly inhibited the expression of adipogenic transcription factors and enzymes, such as CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein α, sterol regulatory element binding protein 1c, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ, acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase, and fatty acid synthase, and increased the expression of phospho-adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase. These results show that bamboo leaf extracts inhibited adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and that the water extract was more efficacious than the ethanol extract.
Keywords: 3T3-L1; Adipocyte; Adipogenesis; Bamboo leaf; Obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
Compliance with ethical standardsThe authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Kopelman PG. Obesity as a medical problem. Nature. 2000;404:635–643. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
