Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction of indigo and indirubin from Isatis indigotica Fort. and their antioxidant capacities
- PMID: 30263665
- PMCID: PMC6049771
- DOI: 10.1007/s10068-017-0112-4
Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction of indigo and indirubin from Isatis indigotica Fort. and their antioxidant capacities
Abstract
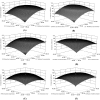
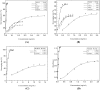
An effective method for the ultrasound-assisted extraction of indigo and indirubin from Isatis indigotica Fort. was established and their antioxidant activities were investigated. Response surface methodology based on a three-level, four-factor Box-Behnken design was used to optimize the extraction conditions. Analysis of variance showed that the quadratic model was significant for the extraction of indigo and indirubin (112.72% ± 1.65% and 116.42% ± 1.27%, respectively) under the optimal conditions (methanol concentration, 80%; extraction time, 25 min; ratio of solid to liquid, 1:34 g/mL; and extraction temperature, 41 °C) and was in good agreement with the predicted value. Moreover, evaluation of the antioxidant activities suggested that indigo and indirubin presented better scavenging effects on 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl free radical and superoxide radical than the extract and the extract revealed certain antioxidant activities in hydroxyl radical scavenging and reducing power, and indigo and indirubin could be used as natural antioxidants in the food or medicine industry.
Keywords: Antioxidant activity; Indigo; Indirubin; Isatis indigotica Fort.; Ultrasound-assisted extraction.
Conflict of interest statement
Compliance with ethical standardsThe authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Angelini LG, Tozzi S, Di Nasso NNO. Differences in leaf yield and indigo precursors production in woad (Isatis tinctoria L.) and Chinese woad (Isatis indigotica Fort.) genotypes. Field Crop Res. 101: 285–295 (2007)
-
- Zheng J, Wang M, Yang X, Wu L. Study on bacteriostasis of Isatis indigotic Fort. Chin J Microecol. 2003;5:18–19.
-
- Xu L, Huang F, Cheng T, Wu J. Antivirus constituents of radix of Isatis Indigotica. Chin J Nat Med. 2005;3:359–360.
-
- Fang J, Tang J, Wang W, Hu Y, Liu Y. Study on chemical fraction with anti-endotoxin activity from Radix Isatidis. Chin Pharm J. 2005;40:1299–1301.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
