Event-related potentials during sustained attention and memory tasks: Utility as biomarkers for mild cognitive impairment
- PMID: 30263929
- PMCID: PMC6156804
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dadm.2018.05.007
Event-related potentials during sustained attention and memory tasks: Utility as biomarkers for mild cognitive impairment
Abstract
Introduction: The objective of the study is to validate attention and memory tasks that elicit event-related potentials (ERPs) for utility as sensitive biomarkers for early dementia.
Methods: A 3-choice vigilance task designed to evaluate sustained attention and standard image recognition memory task designed to evaluate attention, encoding, and image recognition memory were administered with concurrent electroencephalography acquisition to elicit ERPs in mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and healthy cohorts. ERPs were averaged, and mean or maximum amplitude of components was measured and compared between and within cohorts.
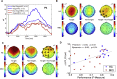
Results: There was significant suppression of the amplitude of the late positive potential in the MCI cohort compared with the healthy controls during 3-choice vigilance task, predominantly over occipital and right temporal-parietal region, and standard image recognition memory task over all regions. During standard image recognition memory task, diminished performance showed strong correlation with electroencephalography measurements. The old/new effects observed in the healthy controls cohort correlated with performance and were lost in MCI.
Discussion: ERPs obtained during cognitive tasks may provide a powerful tool for assessing MCI and have strong potential as sensitive and robust biomarkers for tracking disease progression and evaluating response to investigative therapeutics.
Keywords: Biomarker; Electroencephalography; Event-related potential; Mild cognitive impairment; Neurophysiology.
Figures



References
-
- Sperling R.A., Aisen P.S., Beckett L.A., Bennett D.A., Craft S., Fagan A.M. Toward defining the preclinical stages of Alzheimer's disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer's Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011;7:280–292. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Picton T.W., Bentin S., Berg P., Donchin E., Hillyard S.A., Johnson R., Jr. Guidelines for using human event-related potentials to study cognition: recording standards and publication criteria. Psychophysiology. 2000;37:127–152. - PubMed
-
- Polich J., Ehlers C.L., Otis S., Mandell A.J., Bloom F.E. P300 latency reflects the degree of cognitive decline in dementing illness. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1986;63:138–144. - PubMed
-
- Polich J., Kok A. Cognitive and biological determinants of P300: an integrative review. Biol Psychol. 1995;41:103–146. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
