Know the name: acute epiploic appendagitis-CT findings and review of literature
- PMID: 30264004
- PMCID: PMC6155571
- DOI: 10.21037/acr.2018.02.02
Know the name: acute epiploic appendagitis-CT findings and review of literature
Abstract
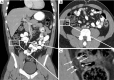
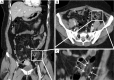
Epiploic appendages are normal pedunculated peritoneal fat containing outpouchings bordering tenia coli on the anti-mesenteric surface of the colon, extending from caecum to the rectosigmoid. Functions are currently unknown, though some postulate them a blood reservoir. The epiploic appendages can become inflamed, with clinical presentations mimicking that of diverticulitis or acute appendicitis. However, unlike acute diverticulitis or appendicitis, epiploic appendagitis are treated conservatively with antibiotics. Currently, the estimated rate of correct preoperative diagnosis of epiploic appendagitis is 2.5%, but due to benign nature of epiploic appendagitis, it is important to appropriately diagnose it preoperatively and thus preventing unnecessary surgical interventions. Clinical features include focal area of pain, often with normal white blood cell count, that often is common in other differential diagnoses. CT scan plays a crucial role in diagnosis and shows an oval fatty density solid lesion along anterior colonic wall surface, surrounded by a rim of fat stranding. Treatment is conservative and involves use of anti-inflammatory medication.
Keywords: Epiploic appendagitis; acute abdomen; appendicitis; computed tomography; diverticulitis; inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Acute Epiploic Appendagitis: An Overlooked Cause of Acute Abdominal Pain.Cureus. 2020 Sep 29;12(9):e10715. doi: 10.7759/cureus.10715. Cureus. 2020. PMID: 33145124 Free PMC article.
-
Acute epiploic appendagitis - a rare differential diagnosis of acute abdomen.Z Gastroenterol. 2023 Feb;61(2):172-177. doi: 10.1055/a-1727-9842. Epub 2022 Dec 5. Z Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 36470286 English.
-
Acute epiploic appendagitis and its mimics.Radiographics. 2005 Nov-Dec;25(6):1521-34. doi: 10.1148/rg.256055030. Radiographics. 2005. PMID: 16284132 Review.
-
Epiploic Appendagitis: An Often Misdiagnosed Cause of Acute Abdomen.Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2019 Sep 5;13(3):364-368. doi: 10.1159/000502683. eCollection 2019 Sep-Dec. Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31607837 Free PMC article.
-
CT imaging findings of epiploic appendagitis: an unusual cause of abdominal pain.Insights Imaging. 2019 Feb 22;10(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s13244-019-0715-9. Insights Imaging. 2019. PMID: 30796645 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epiploic Appendagitis: A Commonly Overlooked Differential of Acute Abdominal Pain.Cureus. 2021 Jan 20;13(1):e12807. doi: 10.7759/cureus.12807. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 33628675 Free PMC article.
-
A False Alarm of Acute Abdomen: Epiploic Appendagitis Case Report and Literature Review.Cureus. 2024 Jul 27;16(7):e65529. doi: 10.7759/cureus.65529. eCollection 2024 Jul. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39188448 Free PMC article.
-
Acute Epiploic Appendagitis: An Overlooked Cause of Acute Abdominal Pain.Cureus. 2020 Sep 29;12(9):e10715. doi: 10.7759/cureus.10715. Cureus. 2020. PMID: 33145124 Free PMC article.
-
Rare causes of acute abdomen and review of literature: Primary/secondary omental torsion, isolated segmental omental necrosis, and epiploic appendagitis.Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2023 Feb;29(2):193-202. doi: 10.14744/tjtes.2022.28430. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2023. PMID: 36748764 Free PMC article.
-
Acute epiploic appendagitis: ultrasound and computed tomography findings of a rare case of acute abdominal pain and the role of other imaging techniques.Pol J Radiol. 2020 Apr 6;85:e178-e182. doi: 10.5114/pjr.2020.94335. eCollection 2020. Pol J Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32419882 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Linkenfeld F. Deutsche Ztschr f Chir. 1908;92:383 10.1007/BF02799591 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
