Estimated Costs of Pivotal Trials for Novel Therapeutic Agents Approved by the US Food and Drug Administration, 2015-2016
- PMID: 30264133
- PMCID: PMC6248200
- DOI: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2018.3931
Estimated Costs of Pivotal Trials for Novel Therapeutic Agents Approved by the US Food and Drug Administration, 2015-2016
Abstract
Importance: A critical question in health care is the extent of scientific evidence that should be required to establish that a new therapeutic agent has benefits that outweigh its risks. Estimating the costs of this evidence of efficacy provides an important perspective.
Objective: To estimate costs and assess scientific characteristics of pivotal efficacy trials that supported the approval of new therapeutic agents by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) from 2015 to 2016.
Design and setting: This study identified 59 novel therapeutic drugs using the annual summary reports from the FDA Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. ClinicalTrials.gov, FDA reviews, and peer-reviewed publications that were publicly available in 2017 were used to identify 52 characteristics of each efficacy trial. Costs were calculated with a global clinical trial cost assessment tool available to contract research organizations and pharmaceutical sponsors.
Main outcomes and measures: Estimated mean cost and 95% CIs based on industry benchmark data from 60 countries. Measures of trials' scientific characteristics included trial design (no control group, placebo, and active drug), end point (surrogate outcome, clinical scale, and clinical outcome), patient enrollment, and treatment duration.
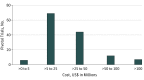
Results: A total of 138 pivotal clinical trials provided the basis for approval of 59 new therapeutic agents by the FDA from 2015 to 2016, with a median estimated cost of $19.0 million (interquartile range, $12.2 million-$33.1 million). Estimated costs ranged from less than $5 million for trials without a control group for 3 orphan drugs with fewer than 15 patients each to $346.8 million (95% CI, $252.0 million-$441.5 million) for a noninferiority trial with end points assessing clinical benefit. Twenty-six of 138 trials (18.8%) were uncontrolled, with a mean estimated cost of $13.5 million (95% CI, $10.1 million-$16.9 million). Trials designed with placebo or active drug comparators had an estimated mean cost of $35.1 million (95% CI, $25.4 million-$44.8 million). Costs also varied by trial end point, treatment duration, patient enrollment, and therapeutic area.
Conclusions and relevance: The highest-cost trials were those in which the new agent had to be proved to be noninferior with clinical benefit end points compared with an agent already available or those that required larger patient populations to achieve statistical power to document smaller treatment effects or accrue infrequently occurring end points.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Clinical Trials-We Get What We Pay For.JAMA Intern Med. 2018 Nov 1;178(11):1457. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2018.3930. JAMA Intern Med. 2018. PMID: 30264093 No abstract available.
References
-
- US Department of Health and Human Services, US Food and Drug Administration Guidance for Industry: Providing Clinical Evidence of Effectiveness for Human Drug and Biological Products. https://www.fda.gov/downloads/drugs/guidancecomplianceregulatoryinformat.... Published May 1998. Accessed May 10, 2018.
-
- US Department of Health and Human Services, US Food and Drug Administration Code of Federal Regulations Title 21: Food and Drugs, Subpart H: accelerated approval of new drugs for serious or life-threatening illnesses. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfcfr/CFRSearch.cfm?C.... Published April 1, 2017. Accessed November 24, 2017.
-
- US Department of Health and Human Services, US Food and Drug Administration Guidance for Industry: Expedited Programs for Serious Conditions–Drugs and Biologics. https://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/Guidances/UCM358301.pdf. Published May 1, 2014. Accessed December 13, 2017.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical