Speech treatment in Parkinson's disease: Randomized controlled trial (RCT)
- PMID: 30264896
- PMCID: PMC6261685
- DOI: 10.1002/mds.27460
Speech treatment in Parkinson's disease: Randomized controlled trial (RCT)
Abstract
Background: As many as 89% of people with Parkinson's disease (PD) develop speech disorders.
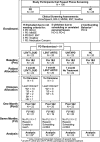
Objectives: This randomized controlled trial evaluated two speech treatments for PD matched in intensive dosage and high-effort mode of delivery, differing in subsystem target: voice (respiratory-laryngeal) versus articulation (orofacial-articulatory).
Methods: PD participants were randomized to 1-month LSVT LOUD (voice), LSVT ARTIC (articulation), or UNTXPD (untreated) groups. Speech clinicians specializing in PD delivered treatment. Primary outcome was sound pressure level (SPL) in reading and spontaneous speech, and secondary outcome was participant-reported Modified Communication Effectiveness Index (CETI-M), evaluated at baseline, 1, and 7 months. Healthy controls were matched by age and sex.
Results: At baseline, the combined PD group (n = 64) was significantly worse than healthy controls (n = 20) for SPL (P < 0.05) and CETI-M (P = 0.0001). At 1 and 7 months, SPL between-group comparisons showed greater improvements for LSVT LOUD (n = 22) than LSVT ARTIC (n = 20; P < 0.05) and UNTXPD (n = 22; P < 0.05). Sound pressure level differences between LSVT ARTIC and UNTXPD at 1 and 7 months were not significant (P > 0.05). For CETI-M, between-group comparisons showed greater improvements for LSVT LOUD and LSVT ARTIC than UNTXPD at 1 month (P = 0.02; P = 0.02). At 7 months, CETI-M between-group differences were not significant (P = 0.08). Within-group CETI-M improvements for LSVT LOUD were maintained through 7 months (P = 0.0011).
Conclusions: LSVT LOUD showed greater improvements than both LSVT ARTIC and UNTXPD for SPL at 1 and 7 months. For CETI-M, both LSVT LOUD and LSVT ARTIC improved at 1 month relative to UNTXPD. Only LSVT LOUD maintained CETI-M improvements at 7 months. © 2018 The Authors. Movement Disorders published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society.
Keywords: Parkinson's disease; RCT; articulation; speech treatment; voice.
© 2018 The Authors. Movement Disorders published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society.
Conflict of interest statement
See relevant conflicts of interest/financial disclosures.
Throughout the active phase of the study, funding was provided by The National Institutes of Health‐National Institute for Deafness and other Communication Disorders (NIH‐NIDCD) (R01 DC01150) through the University of Colorado‐Boulder/National Center for Voice and Speech, the primary place of employment for Ramig (Full Professor), Halpern, and Spielman, and where Fox was a consultant. Freeman was a Full Professor at Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, New York, USA. During poststudy data analysis and manuscript preparation, Ramig, Halpern, and Fox have had employment roles with LSVT Global, and Spielman and Freeman have been paid consultants. Full financial disclosures can be found in the online version of the article.
Figures

References
-
- Logemann JA, Fisher HB, Boshes B, Blonsky ER. Frequency and cooccurrence of vocal tract dysfunctions in the speech of a large sample of Parkinson patients. J Speech Hear Disord 1978;43:47–57. - PubMed
-
- Hartelius L, Svensson P. Speech and swallowing symptoms associated with Parkinson's disease and multiple sclerosis: a survey. Folia Phoniatr Logop 1994;46:9–17. - PubMed
-
- Ho AK, Iansek R, Marigliani C, Bradshaw JL, Gates S. Speech impairment in a large sample of patients with Parkinson's disease. Behav Neurol 1998;11:131–137. - PubMed
-
- Schalling E, Johansson K, Hartelius L. Speech and communication changes reported by people with Parkinson's disease. Folia Phoniatr Logop 2017;69:131–141. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 DC01150/National Institutes of Health-National Institute of Deafness and Other Communication Disorders/International
- R01 DC001150/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- LSVT Global, Inc., Tucson, Arizona/International
- LSVT Global, Inc./International
- R01 DC01150/National Institutes of Health-National Institute of Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIH-NIDCD)/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

