Phototropins of the moss Physcomitrella patens function as blue-light receptors for phototropism in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 30265188
- PMCID: PMC6204831
- DOI: 10.1080/15592324.2018.1525995
Phototropins of the moss Physcomitrella patens function as blue-light receptors for phototropism in Arabidopsis
Abstract
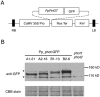
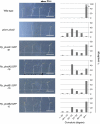
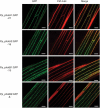
Four phototropin genes (PHOTA1, PHOTA2, PHOTB1, PHOTB2) have been isolated in the moss Physcomitrella patens. These genes encode phototropins that mediate blue-light-induced chloroplast movement. However, the individual functions of these phototropins, including the function of mediating blue-light-induced phototropism, remain unclear. To elucidate the individual functions of P. patens phototropins, each of these phototropin genes was expressed in a phototropin-deficient mutant of Arabidopsis (phot1-5 phot2-1). In addition, fluorescence of GFP fused to these phototropins was examined to determine the subcellular localization of each phototropin. Our results demonstrate that all four P. patens phototropins mediate blue-light-induced phototropism and are associated with the plasma membrane in Arabidopsis. Abbreviations GFP: green fluorescent protein; Pp_phot: Physcomitrella patens phototropin.
Keywords: Phototropism; Physcomitrella; blue light; moss; phototropin; plasma membrane; red light.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Phototropins mediate blue and red light-induced chloroplast movements in Physcomitrella patens.Plant Physiol. 2004 Jul;135(3):1388-97. doi: 10.1104/pp.104.042705. Epub 2004 Jul 9. Plant Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15247376 Free PMC article.
-
Functional characterization of blue-light-induced responses and PHOTOTROPIN 1 gene in Welwitschia mirabilis.J Plant Res. 2016 Mar;129(2):175-87. doi: 10.1007/s10265-016-0790-7. Epub 2016 Feb 8. J Plant Res. 2016. PMID: 26858202
-
Physiological roles of the light, oxygen, or voltage domains of phototropin 1 and phototropin 2 in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol. 2007 Jan;143(1):517-29. doi: 10.1104/pp.106.089839. Epub 2006 Nov 3. Plant Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17085510 Free PMC article.
-
Phototropins 1 and 2: versatile plant blue-light receptors.Trends Plant Sci. 2002 May;7(5):204-10. doi: 10.1016/s1360-1385(02)02245-8. Trends Plant Sci. 2002. PMID: 11992825 Review.
-
Phototropins and blue light-dependent calcium signaling in higher plants.Photochem Photobiol. 2007 Jan-Feb;83(1):102-11. doi: 10.1562/2006-03-08-IR-837. Photochem Photobiol. 2007. PMID: 16906793 Review.
Cited by
-
Machine learning classification of plant genotypes grown under different light conditions through the integration of multi-scale time-series data.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023 May 23;21:3183-3195. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2023.05.005. eCollection 2023. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023. PMID: 37333861 Free PMC article.
-
Light- and hormone-mediated development in non-flowering plants: An overview.Planta. 2020 Nov 27;253(1):1. doi: 10.1007/s00425-020-03501-3. Planta. 2020. PMID: 33245411 Review.
-
Modulation of Phototropin Signalosome with Artificial Illumination Holds Great Potential in the Development of Climate-Smart Crops.Curr Genomics. 2021 Oct 18;22(3):181-213. doi: 10.2174/1389202922666210412104817. Curr Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34975290 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Light and auxin signaling cross-talk programme root development in plants.J Biosci. 2019 Mar;44(1):26. J Biosci. 2019. PMID: 30837377 Review.
References
-
- Darwin C, Darwin F.. The power of movement in plants. New York: D. Appleton; 1881.
-
- Huala E, Teller PW, Liscum E, Han I-S, Larsen E, Briggs WR.. Arabidopsis NPH1: a protein kinase with a putative redox-sensing domain. Science. 1997;278(5346):2120–2123. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
