Activation of mTORC1 signaling in gastric X/A-like cells induces spontaneous pancreatic fibrosis and derangement of glucose metabolism by reducing ghrelin production
- PMID: 30266297
- PMCID: PMC6197745
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.09.027
Activation of mTORC1 signaling in gastric X/A-like cells induces spontaneous pancreatic fibrosis and derangement of glucose metabolism by reducing ghrelin production
Abstract
Background: Pancreatic fibrosis is a pathophysiological process associated with excessive deposition of extracellular matrix in pancreas, leading to reduced insulin secretion and derangement of glucose metabolism. X/A-like cells, a group of unique endocrine cells in gastric oxyntic mucosa, produce and secret ghrelin to influence energy balance. Whether gastric X/A-like cells affect pancreatic fibrosis and subsequent glucose homeostasis remains unclear.
Methods: We established a Ghrl-cre transgene in which the cre enzyme is expressed in X/A-like cells under the control of ghrelin-promoter. TSC1flox/flox mice were bred with Ghrl-cre mice to generate Ghrl-TSC1-/- (TG) mice, within which mTORC1 signaling was activated in X/A-like cells. Pancreatic fibrosis and insulin secretion were analyzed in the TG mice.
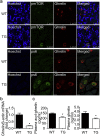
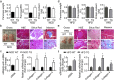
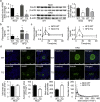
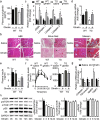
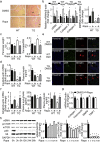
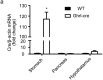
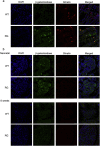
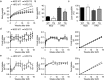
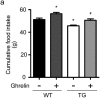
Findings: Activation of mTORC1 signaling by deletion of TSC1 gene in gastric X/A-like cells induced spontaneous pancreatic fibrosis. This alteration was associated with reduced insulin expression and secretion, as well as impaired glucose metabolism. Activation of mTORC1 signaling in gastric X/A-like cells reduced gastric and circulating ghrelin levels. Exogenous ghrelin reversed pancreatic fibrosis and glucose intolerance induced by activation of mTORC1 signaling in these cells. Rapamycin, an inhibitor of mTOR, reversed the decrease of ghrelin levels and pancreatic fibrosis.
Interpretation: Activation of mTORC1 signaling in gastric X/A-like cells induces spontaneous pancreatic fibrosis and subsequently impairs glucose homeostasis via suppression of ghrelin.
Keywords: Fibrosis; Ghrelin; Glucose metabolism; Matrix metalloproteinases; Pancreatic islets.
Copyright © 2018. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures

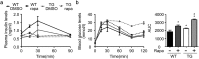
Similar articles
-
mTOR Signaling in X/A-Like Cells Contributes to Lipid Homeostasis in Mice.Hepatology. 2019 Feb;69(2):860-875. doi: 10.1002/hep.30229. Epub 2018 Dec 31. Hepatology. 2019. PMID: 30141265 Free PMC article.
-
The cannabinoid CB1 receptor and mTORC1 signalling pathways interact to modulate glucose homeostasis in mice.Dis Model Mech. 2016 Jan;9(1):51-61. doi: 10.1242/dmm.020750. Epub 2015 Nov 12. Dis Model Mech. 2016. PMID: 26563389 Free PMC article.
-
Transgenic overexpression of intraislet ghrelin does not affect insulin secretion or glucose metabolism in vivo.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2012 Feb 15;302(4):E403-8. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00341.2011. Epub 2011 Nov 22. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2012. PMID: 22114024
-
Ghrelin is a physiological regulator of insulin release in pancreatic islets and glucose homeostasis.Pharmacol Ther. 2008 May;118(2):239-49. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2008.02.008. Epub 2008 Mar 10. Pharmacol Ther. 2008. PMID: 18433874 Review.
-
The role of ghrelin in the regulation of glucose homeostasis.Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2016 Apr 1;26(1):3-11. doi: 10.1515/hmbci-2016-0018. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2016. PMID: 27235674 Review.
Cited by
-
Ghrelin Based Therapy of Metabolic Diseases.Curr Med Chem. 2021;28(13):2565-2576. doi: 10.2174/0929867327666200615152804. Curr Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 32538716 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stomach 'tastes' the food and adjusts its emptying: A neurophysiological hypothesis (Review).Exp Ther Med. 2020 Sep;20(3):2392-2395. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.8874. Epub 2020 Jun 11. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 32765721 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ghrelin Fights Against Titanium Particle-Induced Inflammatory Osteolysis Through Activation of β-Catenin Signaling Pathway.Inflammation. 2019 Oct;42(5):1652-1665. doi: 10.1007/s10753-019-01026-w. Inflammation. 2019. PMID: 31165326
-
Intestinal Enteroendocrine Cells: Present and Future Druggable Targets.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 16;24(10):8836. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108836. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37240181 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lower ghrelin levels does not impact the metabolic benefit induced by Roux-en-Y gastric bypass.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Aug 23;13:891379. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.891379. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36082078 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rockey D.C., Bell P.D., Hill J.A. Fibrosis--a common pathway to organ injury and failure. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(12):1138–1149. - PubMed
-
- Tran T.C., Van'T Hof G., Kazemier G. Pancreatic fibrosis correlates with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency after pancreatoduodenectomy. Dig Surg. 2008;25(4):311–318. - PubMed
-
- Kopelman H., Corey M., Gaskin K., Durie P., Weizman Z., Forstner G. Impaired chloride secretion, as well as bicarbonate secretion, underlies the fluid secretory defect in the cystic fibrosis pancreas. Gastroenterology. 1988;95(2):349–355. - PubMed
-
- Kopelman H., Durie P., Gaskin K., Weizman Z., Forstner G. Pancreatic fluid secretion and protein hyperconcentration in cystic fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 1985;312(6):329–334. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

