Dual Targeting of Aurora Kinases with AMG 900 Exhibits Potent Preclinical Activity Against Acute Myeloid Leukemia with Distinct Post-Mitotic Outcomes
- PMID: 30266802
- PMCID: PMC6279493
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-18-0186
Dual Targeting of Aurora Kinases with AMG 900 Exhibits Potent Preclinical Activity Against Acute Myeloid Leukemia with Distinct Post-Mitotic Outcomes
Abstract
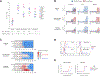
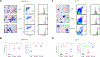
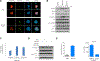
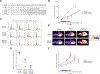
Aurora kinase A and B have essential and non-overlapping roles in mitosis, with elevated expression in a subset of human cancers, including acute myeloid leukemia (AML). In this study, pan-aurora kinase inhibitor (AKI) AMG 900 distinguishes itself as an anti-leukemic agent that is more uniformly potent against a panel of AML cell lines than are isoform-selective AKIs and classic AML drugs. AMG 900 inhibited AML cell growth by inducing polyploidization and/or apoptosis. AMG 900 and aurora-B-selective inhibitor AZD1152-hQPA showed comparable cellular effects on AML lines that do not harbor a FLT3-ITD mutation. AMG 900 was active against P-glycoprotein-expressing AML cells resistant to AZD1152-hQPA and was effective at inducing expression of megakaryocyte-lineage markers (CD41, CD42) on human CHRF-288-11 cells and mouse Jak2 V617F cells. In MOLM-13 cells, inhibition of p-histone H3 by AMG 900 was associated with polyploidy, extra centrosomes, accumulation of p53 protein, apoptosis, and cleavage of Bcl-2 protein. Co-administration of cytarabine (Ara-C) with AMG 900 potentiated cell killing in a subset of AML lines, with evidence of attenuated polyploidization. AMG 900 inhibited the proliferation of primary human bone marrow cells in culture, with a better proliferation recovery profile relative to classic antimitotic drug docetaxel. In vivo, AMG 900 significantly reduced tumor burden in a systemic MOLM-13 xenograft model where we demonstrate the utility of 3'-deoxy-3'-18F-fluorothymidine [18F]FLT positron emission tomographic (PET)-CT imaging to measure the antiproliferative effects of AMG 900 in skeletal tissues in mice.
©2018 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest. M. Payton, K. Cheung, W. Wayne, K. Hanestad, G. Juan, and A. Coxon are current or former full-time employees of Amgen Inc. and have owned stock in Amgen Inc. at the time this work was conducted. No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed by the other authors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Preclinical evaluation of AMG 900, a novel potent and highly selective pan-aurora kinase inhibitor with activity in taxane-resistant tumor cell lines.Cancer Res. 2010 Dec 1;70(23):9846-54. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-3001. Epub 2010 Oct 8. Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20935223
-
Preclinical evaluation of the Aurora kinase inhibitors AMG 900, AZD1152-HQPA, and MK-5108 on SW-872 and 93T449 human liposarcoma cells.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2018 Jan;54(1):71-84. doi: 10.1007/s11626-017-0208-4. Epub 2017 Dec 1. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2018. PMID: 29197031
-
The FLT3 internal tandem duplication mutation is a secondary target of the aurora B kinase inhibitor AZD1152-HQPA in acute myelogenous leukemia cells.Mol Cancer Ther. 2010 Mar;9(3):661-72. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-09-1144. Epub 2010 Feb 16. Mol Cancer Ther. 2010. PMID: 20159992
-
Antineoplastic effects of an Aurora B kinase inhibitor in breast cancer.Mol Cancer. 2010 Feb 22;9:42. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-9-42. Mol Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20175926 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of the aurora kinase inhibitors AZD1152-HQPA and ZM447439 on growth arrest and polyploidy in acute myeloid leukemia cell lines and primary blasts.Haematologica. 2008 May;93(5):662-9. doi: 10.3324/haematol.12148. Epub 2008 Mar 26. Haematologica. 2008. PMID: 18367484
Cited by
-
Stress-Induced Polyploid Giant Cancer Cells: Unique Way of Formation and Non-Negligible Characteristics.Front Oncol. 2021 Aug 30;11:724781. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.724781. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34527590 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The balance between mitotic death and mitotic slippage in acute leukemia: a new therapeutic window?J Hematol Oncol. 2019 Nov 26;12(1):123. doi: 10.1186/s13045-019-0808-4. J Hematol Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31771633 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rationale, in silico docking, ADMET profile, design, synthesis and cytotoxicity evaluations of phthalazine derivatives as VEGFR-2 inhibitors and apoptosis inducers.RSC Adv. 2024 Aug 27;14(37):27110-27121. doi: 10.1039/d4ra04956j. eCollection 2024 Aug 22. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39193307 Free PMC article.
-
Aurora Kinase B Inhibition: A Potential Therapeutic Strategy for Cancer.Molecules. 2021 Apr 1;26(7):1981. doi: 10.3390/molecules26071981. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33915740 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Editorial: Genetics and Molecular Mechanisms of Oral and Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2022 Apr 6;12:874353. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.874353. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35463329 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA: A Cancer J for Clinicians. 2015;65:5–29. - PubMed
-
- Dohner H, Weisdorf DJ, Bloomfield CD. Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N Engl. J Med 2015;373:1137–51. - PubMed
-
- Laubach J, Rao AV. Current and emerging strategies for the management of acute myeloid leukemia in the elderly. The Oncologist 2008;13:1097–1108. - PubMed
-
- Lens SM, Voest EE, Medema RH. Shared and separate functions of polo-like kinases and aurora kinases in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010;10:825–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

