On-chip spatiotemporal electrophysiological analysis of human stem cell derived cardiomyocytes enables quantitative assessment of proarrhythmia in drug development
- PMID: 30266924
- PMCID: PMC6162288
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-32921-1
On-chip spatiotemporal electrophysiological analysis of human stem cell derived cardiomyocytes enables quantitative assessment of proarrhythmia in drug development
Abstract
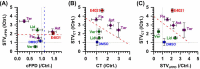
We examined a simultaneous combined spatiotemporal field potential duration (FPD) and cell-to-cell conduction time (CT) in lined-up shaped human embryonic stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes (hESC-CMs) using an on-chip multielectrode array (MEA) system to evaluate two origins of lethal arrhythmia, repolarization and depolarization. The repolarization index, FPD, was prolonged by E-4031 and astemizole, and shortened by verapamil, flecainide and terfenadine at 10 times higher than therapeutic plasma concentrations of each drug, but it did not change after lidocaine treatment up to 100 μM. CT was increased by astemizol, flecainide, terfenadine, and lidocaine at equivalent concentrations of Nav1.5 IC50, suggesting that CT may be an index of cardiac depolarization because the increase in CT (i.e., decrease in cell-to-cell conduction speed) was relevant to Nav1.5 inhibition. Fluctuations (short-term variability; STV) of FPD and CT, STVFPD and STVCT also discriminated between torsadogenic and non-torsadogenic compounds with significant increases in their fluctuation values, enabling precise prediction of arrhythmogenic risk as potential new indices.
Conflict of interest statement
A part of the authors (Yu.A., Ya.A., K.T. and A.S.) are employees of Daiichi-Sankyo Co. Ltd. All the other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Ando Hiroyuki, Yoshinaga Takashi, Yamamoto Wataru, Asakura Keiichi, Uda Takaaki, Taniguchi Tomohiko, Ojima Atsuko, Shinkyo Raku, Kikuchi Kiyomi, Osada Tomoharu, Hayashi Seiji, Kasai Chieko, Miyamoto Norimasa, Tashibu Hiroyuki, Yamazaki Daiju, Sugiyama Atsushi, Kanda Yasunari, Sawada Kohei, Sekino Yuko. A new paradigm for drug-induced torsadogenic risk assessment using human iPS cell-derived cardiomyocytes. Journal of Pharmacological and Toxicological Methods. 2017;84:111–127. doi: 10.1016/j.vascn.2016.12.003. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kitaguchi Takashi, Moriyama Yuta, Taniguchi Tomohiko, Ojima Atsuko, Ando Hiroyuki, Uda Takaaki, Otabe Koji, Oguchi Masao, Shimizu Shigekazu, Saito Hiroyuki, Morita Maya, Toratani Atsushi, Asayama Mahoko, Yamamoto Wataru, Matsumoto Emi, Saji Daisuke, Ohnaka Hiroki, Tanaka Kohji, Washio Ikumi, Miyamoto Norimasa. CSAHi study: Evaluation of multi-electrode array in combination with human iPS cell-derived cardiomyocytes to predict drug-induced QT prolongation and arrhythmia — Effects of 7 reference compounds at 10 facilities. Journal of Pharmacological and Toxicological Methods. 2016;78:93–102. doi: 10.1016/j.vascn.2015.12.002. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

