Antimicrobial genes from Allium sativum and Pinellia ternata revealed by a Bacillus subtilis expression system
- PMID: 30266995
- PMCID: PMC6162269
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-32852-x
Antimicrobial genes from Allium sativum and Pinellia ternata revealed by a Bacillus subtilis expression system
Abstract
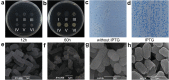
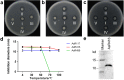
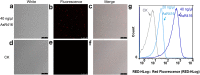
Antimicrobial genes are found in all classes of life. To efficiently isolate these genes, we used Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli as target indicator bacteria and transformed them with cDNA libraries. Among thousands of expressed proteins, candidate proteins played antimicrobial roles from the inside of the indicator bacteria (internal effect), contributing to the sensitivity (much more sensitivity than the external effect from antimicrobial proteins working from outside of the cells) and the high throughput ability of screening. We found that B. subtilis is more efficient and reliable than E. coli. Using the B. subtilis expression system, we identified 19 novel, broad-spectrum antimicrobial genes. Proteins expressed by these genes were extracted and tested, exhibiting strong external antibacterial, antifungal and nematicidal activities. Furthermore, these newly isolated proteins could control plant diseases. Application of these proteins secreted by engineered B. subtilis in soil could inhibit the growth of pathogenic bacteria. These proteins are thermally stable and suitable for clinical medicine, as they exhibited no haemolytic activity. Based on our findings, we speculated that plant, animal and human pathogenic bacteria, fungi or even cancer cells might be taken as the indicator target cells for screening specific resistance genes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Isolation of Antimicrobial Genes from Oryza rufipogon Griff by Using a Bacillus subtilis Expression System with Potential Antimicrobial Activities.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 18;21(22):8722. doi: 10.3390/ijms21228722. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33218175 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the mechanism of antimicrobial action of the gold(I) compound auranofin in Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Nov 5;12(11):e0013824. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00138-24. Epub 2024 Oct 8. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 39377597 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced Nicotiana benthamiana immune responses caused by heterologous plant genes from Pinellia ternata.BMC Plant Biol. 2018 Dec 17;18(1):357. doi: 10.1186/s12870-018-1598-5. BMC Plant Biol. 2018. PMID: 30558544 Free PMC article.
-
Exploitation of Bacillus subtilis as a robust workhorse for production of heterologous proteins and beyond.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018 Sep 10;34(10):145. doi: 10.1007/s11274-018-2531-7. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 30203131 Review.
-
Antimicrobial Peptides from Plants: A cDNA-Library Based Isolation, Purification, Characterization Approach and Elucidating Their Modes of Action.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 13;22(16):8712. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168712. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445412 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Integrated physicochemical, hormonal, and transcriptomic analysis reveals the underlying mechanism of callus formation in Pinellia ternata hydroponic cuttings.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Jun 20;14:1189499. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1189499. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37409296 Free PMC article.
-
Cell Membrane-Interrupting Antimicrobial Peptides from Isatis indigotica Fortune Isolated by a Bacillus subtilis Expression System.Biomolecules. 2019 Dec 24;10(1):30. doi: 10.3390/biom10010030. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31878275 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Deoxynivalenol-Activated Wheat Arl6ip4 Gene Encodes an Antifungal Peptide with Deoxynivalenol Affinity and Protects Plants against Fusarium Pathogens and Mycotoxins.J Fungi (Basel). 2021 Nov 6;7(11):941. doi: 10.3390/jof7110941. J Fungi (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34829228 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction and Activity of a Cationic α-Helix Antimicrobial Peptide ZM-804 from Maize.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 5;22(5):2643. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052643. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33807972 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation of Potato Endophytes and Screening of Chaetomium globosum Antimicrobial Genes.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 21;23(9):4611. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094611. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563004 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

