Population Pharmacokinetics and Exploratory Exposure-Response Relationships of Diazepam in Children Treated for Status Epilepticus
- PMID: 30267478
- PMCID: PMC6263663
- DOI: 10.1002/psp4.12349
Population Pharmacokinetics and Exploratory Exposure-Response Relationships of Diazepam in Children Treated for Status Epilepticus
Abstract
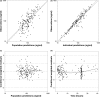
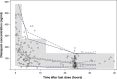
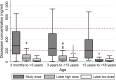
Diazepam is labeled for status epilepticus (SE) in children, but there are limited data characterizing its disposition in pediatric patients. We developed a population pharmacokinetic (PK) model of i.v. diazepam in children with SE. We evaluated relationships between PK parameters and both safety and efficacy, and simulated exposures using dosing regimens from the product label and clinical practice. The model was developed using prospective data from a pediatric clinical trial comparing diazepam to lorazepam for treatment of SE. Altogether, 87 patients aged ≥ 3 months to < 18 years contributed 162 diazepam concentrations. Diazepam PKs were well characterized by a two-compartment model scaled by body size. No significant or clinically important relationships were observed between diazepam PKs and safety or efficacy. Simulations demonstrated that, compared with label dosing, the study dose (0.2 mg/kg i.v., maximum 8 mg) resulted in greater frequency in rapidly achieving the target therapeutic range of 200-600 ng/mL.
© 2018 The Authors CPT: Pharmacometrics & Systems Pharmacology published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of the American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Population Pharmacokinetics and Exploratory Pharmacodynamics of Lorazepam in Pediatric Status Epilepticus.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2017 Aug;56(8):941-951. doi: 10.1007/s40262-016-0486-0. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2017. PMID: 27943220 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Lorazepam v. diazepam for pediatric status epilepticus.CJEM. 2016 May;18(3):235-8. doi: 10.1017/cem.2015.66. Epub 2015 Jul 6. CJEM. 2016. PMID: 26143942
-
Lorazepam versus diazepam-phenytoin combination in the treatment of convulsive status epilepticus in children: a randomized controlled trial.Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2010 Mar;14(2):162-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpn.2009.02.004. Epub 2009 Mar 18. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2010. PMID: 19297221 Clinical Trial.
-
A Comparison of Midazolam, Lorazepam, and Diazepam for the Treatment of Status Epilepticus in Children: A Network Meta-analysis.J Child Neurol. 2016 Aug;31(9):1093-107. doi: 10.1177/0883073816638757. Epub 2016 Mar 28. J Child Neurol. 2016. PMID: 27021145 Review.
-
Best evidence topic reports. Lorazepam or diazepam in paediatric status epilepticus.Emerg Med J. 2006 Jun;23(6):472-3. doi: 10.1136/emj.2006.037606. Emerg Med J. 2006. PMID: 16714516 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
A pharmacokinetic simulation study to assess the performance of a sparse blood sampling approach to quantify early drug exposure.Clin Transl Sci. 2021 Jul;14(4):1444-1451. doi: 10.1111/cts.13004. Epub 2021 May 1. Clin Transl Sci. 2021. PMID: 33742783 Free PMC article.
-
Expansion of a Pharmacokinetic Model for Diazepam to Characterize Real-World IV and Oral Data in Children With and Without Obesity.J Clin Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 28:10.1002/jcph.70027. doi: 10.1002/jcph.70027. Online ahead of print. J Clin Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40289640
References
-
- Sofou, K. , Kristjánsdóttir, R. , Papachatzakis, N.E. , Ahmadzadeh, A. & Uvebrant, P. Management of prolonged seizures and status epilepticus in childhood: a systematic review. J. Child Neurol. 24, 918–926 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Neville, B.G.R. , Chin, R.F.M. & Scott, R.C. Childhood convulsive status epilepticus: epidemiology, management and outcome. Acta Neurol. Scand. Suppl. 186, 21–24 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Raspall‐Chaure, M. , Chin, R.F. , Neville, B.G. & Scott, R.C. Outcome of paediatric convulsive status epilepticus: a systematic review. Lancet Neurol. 5, 769–779 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Lowenstein, D.H. & Alldredge, B.K. Status epilepticus at an urban public hospital in the 1980s. Neurology 43, 483–488 (1993). - PubMed
-
- De Negri, M. & Baglietto, M.G. Treatment of status epilepticus in children. Paediatr. Drugs 3, 411–420 (2001). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

