Insights From Antiviral Therapy Into Immune Responses to Hepatitis B and C Virus Infection
- PMID: 30267712
- PMCID: PMC6340757
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.08.061
Insights From Antiviral Therapy Into Immune Responses to Hepatitis B and C Virus Infection
Abstract
There are 257 million persons worldwide with chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, a leading causes of liver cancer. Almost all adults with acute HBV infection have a rapid immune response to the virus, resulting in life-long immunity, but there is no cure for individuals with chronic HBV infection, which they acquire during early life. The mechanisms that drive the progression of HBV through distinct clinical phases to end-stage liver disease are poorly understood. Likewise, it is not clear whether and how immune responses can be modulated to allow control and/or clearance of intrahepatic HBV DNA. We review the innate and adaptive immune responses to acute and chronic HBV infections and responses to antiviral therapy. Comparisons with hepatitis C virus infection provide insights into the reversibility of innate inflammatory responses and the potential for successful therapy to recover virus-specific memory immune responses.
Keywords: Hepatitis B Virus; Hepatitis C Virus; Immune Memory; Innate.
Copyright © 2019 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
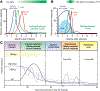

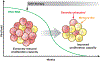
References
-
- Blumberg BS. Hepatitis B - The hunt for a killer virus: Princeton University Press, 2002.
-
- Chiang CJ, Yang YW, You SL, et al. Thirty-year outcomes of the national hepatitis B immunization program in Taiwan. JAMA 2013;310:974–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

