Smoking-Induced SLPI Expression Hinders HPV Infections Also in Squamous Cell Carcinomas of the Vulva
- PMID: 30267960
- PMCID: PMC6161366
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tranon.2018.09.004
Smoking-Induced SLPI Expression Hinders HPV Infections Also in Squamous Cell Carcinomas of the Vulva
Abstract
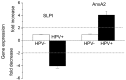
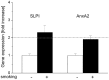
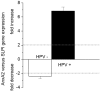
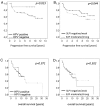
In HNSCC, protein- and mRNA-expression of the antileukoproteinase SLPI are significantly inverse correlated with HPV-infection suggesting that elevated expression of SLPI protects against HPV-infections. Moreover, SLPI-expression is up-regulated in HNSCC-patients reporting a smoking habit. Here, we investigate the described correlation in other HPV-driven cancers, namely vulvar squamous cell carcinoma (VSCC). FFPE samples of 99 VSCC were analyzed by PCR for HPV-DNA-expression and by RT-qPCR for SLPI-mRNA-expression. Of 99 VSCC 10 (10.1%) are HPV-positive; 9 were HPV16; 1 HPV18; all were E6/E7 mRNA-positive. 33 of the 99 patients (33.3%) reported a smoking habit; 7 (21.1%) of these were HPV-positive. Of 66 (66.7%) non-smokers 3 (4.5%) were HPV-positive. SLPI-expression was 4.0-fold lower in HPV-positive than HPV-negative patients. Smoking resulted in 2.3-fold higher SLPI expression. The data presented here indicate that SLPI plays a pivotal role in HPV-infection not only in HNSCC but also in VSCC and possibly also in other HPV-driven cancers. This however, needs to be analyzed in future studies. Furthermore these data lead to the hypothesis that the smoking induced SLPI-increase is systemic rather than local, as assumed based on the HNSCC data.
Copyright © 2018. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
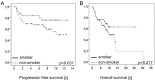
References
-
- Quabius ES, Haag J, Kuhnel A, Henry H, Hoffmann AS, Gorogh T, Hedderich J, Evert M, Beule AG, Maune S. Geographical and anatomical influences on human papillomavirus prevalence diversity in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma in Germany. Int J Oncol. 2015;46:414–422. - PubMed
-
- Hoffmann M, Ihloff AS, Gorogh T, Weise JB, Fazel A, Krams M, Rittgen W, Schwarz E, Kahn T. p16(INK4a) overexpression predicts translational active human papillomavirus infection in tonsillar cancer. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:1595–1602. - PubMed
-
- Klussmann JP, Weissenborn SJ, Wieland U, Dries V, Eckel HE, Pfister HJ, Fuchs PG. Human papillomavirus-positive tonsillar carcinomas: a different tumor entity? Med Microbiol Immunol. 2003;192:129–132. - PubMed
-
- Prigge ES, von Knebel DM, Reuschenbach M. Clinical relevance and implications of HPV-induced neoplasia in different anatomical locations. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2017;772:51–66. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

