Neuromyelitis optica with unilateral diaphragmatic paralysis
- PMID: 30269091
- PMCID: PMC6169650
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2018-225984
Neuromyelitis optica with unilateral diaphragmatic paralysis
Abstract
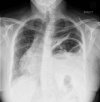
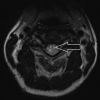
In this case report, we describe the course of a female patient who is known to have neuromyelitis optica (NMO) and developed left hemiparesis and unilateral diaphragmatic paralysis. She was initially treated with intravenous methylprednisolone 1 g daily for 5 days without improvement. Subsequently, she received five sessions of a plasmapheresis. Her hemiparesis had improved after few days. however, the phrenic nerve palsy remained.
Keywords: neurology; respiratory system.
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2018. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
